Social Networks Week 5 Nptel Assignment Answers
Are you looking for Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers ? You are here at right place for Week 1 assignment answers
Table of Contents

Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment Answers (July-Dec 2025)
Question 1. For threshold t = 3, how many same-culture neighbors does a family need to remain content?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 4
Question 2. If the threshold were lowered from 3 to 1, what is likely to happen to the neighborhood pattern?
a) It will become more mixed (fewer moves)
b) It will become more segregated (more moves)
c) It will remain unchanged
d) All families will move out
Question 3. Which effect is expected when all families increase their threshold (e.g., from 1 to 3)?
a) Fewer relocations
b) More relocations
c) No relocations
d) No predictable change
Question 4. Which of these configurations represents strong segregation (given a high threshold)?
a) Red and blue homes alternating regularly
b) One contiguous cluster of reds and one of blues
c) A checkerboard of red/blue
d) A random mix of reds and blues
Question 5. Which factors tend to increase spatial segregation?
a) Higher relocation thresholds (more moves needed)
b) More empty houses available to move into
c) Fewer same-culture neighbors nearby (families unsatisfied)
d) Pre-existing pockets of similar families in the grid
Question 6. Why are empty houses included in the Schelling simulation?
a) To allow families to relocate into them
b) To represent unemployed families
c) To reduce neighborhood density
d) To buffer interactions between groups
Question 7. If each house has 8 neighbors and threshold t = 0.5, how many same-color neighbors are needed to be satisfied?
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
d) 6
Question 8. What happens if t = 0 (no preference) for all families?
a) No one moves (everyone is content)
b) Everyone moves at least once
c) Movements continue indefinitely
d) Families swap places forever
Question 9. According to Schelling’s findings, which statements are true?
a) Even moderate neighbor preferences can lead to strong segregation
b) Many empty houses prevent any relocations
c) A zero threshold (t = 0) means no relocation is needed
d) A fully segregated state always occurs eventually
Question 10. Which issues can prevent the simulation from reaching all families satisfied?
a) Too few empty houses available to move into
b) Threshold t that is too high for the given mix
c) The grid being disconnected (no neighbor relationships)
d) A zero threshold t = 0
Question 11. In this signed network, a negative edge between two people indicates:
a) They are friends
b) They are antagonistic/enemies
c) They have no relationship
d) It has no meaning
Question 12. In a complete group of 5 people (all connected), suppose there are 2 negative edges. How many positive edges are there?
a) 7
b) 8
c) 9
d) 10
Question 13. In the adjacency matrix representation, a negative tie is usually denoted by:
a) +1
b) –1
c) 0
d) 2
Question 14. If A–B = + and B–C = –, what is the implied overall sentiment from A to C (via B)?
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Neutral
d) Undetermined
Question 15. Which of the following describe negative edges?
a) They indicate enmity or antagonism
b) They are represented as –1 in the adjacency matrix
c) They indicate a strong friendship
d) They indicate a neutral/weak tie
Question 16. Which of these triangles (edge signs) are balanced?
a) + + + (3 positives)
b) + + – (2 positives, 1 negative)
c) + – – (1 positive, 2 negatives)
d) – – – (0 positives)
Question 17. In a balanced triangle, the number of negative edges can be:
a) 0 or 2
b) 1
c) Only 0
d) Only 3
Question 18. Which global outcomes reflect a structurally balanced network?
a) All individuals are mutual friends (+ between all)
b) The group splits into exactly two factions with only inter-group hostility
c) Every triangle in the network has two positive edges
d) Everyone is mutual enemies (all –)
Question 19. If a triangle has all three relationships negative (A–B = –, B–C = –, A–C = –), structural balance theory predicts:
a) Two of them will become friends (one – changes to +)
b) All three remain enemies indefinitely
c) All three will become friends (+)
d) This situation is already stable
Question 20. Which of the following triangles are unbalanced?
a) + + +
b) + + –
c) + – –
d) – – –
Question 21. According to the Balance Theorem, a balanced complete graph can have at most how many antagonistic blocs?
a) 1
b) 2
c) 3
d) 5
Question 22. If a network of 5 countries is balanced and not all edges are positive, what must be true?
a) It splits into exactly two hostile coalitions
b) All edges are negative
c) Some cycle of 3 countries has 2 positive edges
d) The network must be disconnected
Question 23. Which conditions hold in any balanced complete network?
a) No triangle has exactly two positive ties
b) The nodes can be partitioned into two groups
c) Every edge in the graph is positive
d) All negative edges are between the two groups
Question 24. Which scenarios indicate the network is not balanced?
a) A triangle with 2 positive and 1 negative edge
b) All edges in the network are positive
c) A triangle with 0 positives (all 3 negative)
d) Nodes are separable into two groups with only inter-group enmity
Question 25. In a balanced network of 5 nodes split into groups of 2 and 3, how many positive edges exist?
a) 4
b) 5
c) 6
d) 7
Question 26. In an ideal two-coalition split, which condition holds?
a) All ties within each team are positive, and all across teams are negative
b) No ties are cut by the partition
c) Exactly half the positive ties must cross between teams
d) Each team has equal size
Question 27. Which strategy exemplifies a greedy heuristic for forming the coalitions?
a) Start with a random division, then iteratively move individuals if it increases satisfied ties
b) Group alphabetically by name
c) Put all friends in one team and ignore conflicts
d) Form one team as all positive nodes and the other all negative
Question 28. Splitting nodes to maximize separation of negative ties is equivalent to which classical problem?
a) Maximum cut on the negative-edge subgraph
b) Minimum spanning tree
c) Clique cover
d) Hamiltonian cycle
Question 29. In a triangle with A–B = +, B–C = +, and A–C = –, which groupings form balanced teams?
a) {A,B} and {C}
b) {B,C} and {A}
c) {A,C} and {B}
d) {A,B,C} (all together)
Question 30. Which of the following describe characteristics of an optimal two-team partition?
a) Positive ties are maximized within each team
b) Internal negative ties are minimized
c) All negative ties end up within teams
d) Negative ties lie between the two teams
Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment Answers (Jan-Apr 2025)
Q1. Which of the following is a key factor contributing to spatial segregation in a Schelling model?
a) Random movement of individuals
b) Preference for neighbours of similar characteristics
c) Strong central nodes in the network
d) High clustering coefficients in social graphs
Q2. In spatial segregation, increasing the tolerance threshold in the Schelling model typically leads to:
a) Increased segregation
b) Reduced segregation
c) No change in segregation patterns
d) Complete randomization of the system
Q3. The Schelling model of segregation assumes that individuals:
a) Move randomly to new locations
b) Relocate only when dissatisfied with their neighbors
c) Always maximize their number of neighbors
d) Form coalitions based on strong preferences
Q4. Which of the following best explains why the Schelling model exhibits segregation even with low intolerance levels?
a) Random noise in movement
b) Positive feedback loops in local preferences
c) Network centrality biases
d) Global optimization strategies
Q5. In structural balance theory, a triad with one positive edge and two negative edges is:
a) Balanced
b) Unbalanced
c) Neutral
d) Impossible in theory
Q6. What does a negative relationship in structural balance theory typically signify in a graph?
a) Cooperation between nodes
b) Dislike or rivalry between nodes
c) A lack of a connection
d) A mediator between two balanced nodes
Q7. The structural balance theorem states that a graph is balanced if it can be split into:
a) Two subgraphs with only positive edges within each subgraph and only negative edges between them
b) A single graph with all positive edges
c) Multiple subgraphs with both positive and negative edges
d) A graph with equal positive and negative edges
Q8. Which of the following triads is unbalanced according to structural balance theory?
a) All positive edges
b) One positive edge and two negative edges
c) Two positive edges and one negative edge
d) All negative edges
Q9. To characterize the balance of a structural graph, one commonly evaluates:
a) Degree centrality of nodes
b) The ratio of balanced to unbalanced triads
c) The number of connected components
d) Clustering coefficients of all nodes
Q10. In coalition formation theory, which of the following is most important for stable coalitions in a network?
a) The clustering coefficient of the graph
b) The balance between positive and negative relationships within the coalition
c) The degree centrality of individual members
d) The total number of triads in the network
Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 4 Answers (JULY-DEC 2023)
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q1. Which of the following network is structurally balanced?
Network A only
Network B only
Both Network A and B
Neither Network A nor B
Answer: Network A only
Q2. Suppose P, Q and R represent three individuals with either of the two relationships, a friendship shown as ‘+’ symbol or enmity shown as ‘-’ symbol. Which one of the following structures is balanced?
(A) only
(B) only
(C) only
Both (A) and (C)
Answer: (A) only
Q3. Two of my close friends hate each other. In how many ways can the structure evolve to a stable configuration?
1
2
3
It is already stable
Answer: 3
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q4. Given the solid edges indicate positive ties and dotted edges indicate negative ties, which of the following graphs is stable?
(a) only
(b) only
(c) only
All the above
Answer: (a) only
Q5. In a graph having 6 nodes, how many possible edges can be present?
15
30
42
21
Answer: 15
Q6. Given threshold t=5, which of the following configuration is stable in the schelling’s model?
(A) only
(B) only
Both (A) and (B)
None of the above
Answer: None of the above
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q7. When is a signed triangle said to be unstable?
zero positive edges
3 positive edges
even number of positive edges
odd number of positive edges
Answer: even number of positive edges
Q8. Can we have a complete signed graph on 4 nodes (K4) and 5 nodes (K5) respectively, each having exactly one unstable triangle respectively?
No, No
No, Yes
Yes, No
Yes, Yes
Answer: No, No
Q9. Consider Schelling model for a x×x grid. What is the minimum value of x such that there is at least one person having at least 8 neighbours? You can assume that no cell is empty.
2
3
4
5
Answer: 3
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q10. Which of the following real-life cliche holds true in terms of structural balance in networks?
Enemy’s enemy is an enemy
Enemy’s enemy is a friend
Birds of the same feather flock together
We follow each other
Answer: Enemy’s enemy is a friend
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
More Weeks of Social Networks: Click here
More Nptel Courses: Click here
Session: JAN-APR 2023
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q1. Which of the following is an invalid value for the two dimensional Schelling model grid?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 9
Answer: d. 9
Q2. Given a triangular network with two positive relationships, When is the network stable?
a. Never
b. Sometimes
c. Always
d. cannot be inferred
Answer: b. Sometimes
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q3. Given the two dimensional grid in Figure 1, comment on the stability of the node in the center for A and B, given threshold t=2.
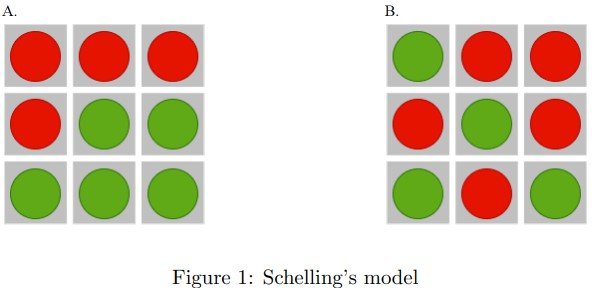
a. unstable, unstable
b. unstable, stable
c. stable, unstable
d. stable, stable
Answer: d. stable, stable
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q4. For a graph with five nodes, what is the maximum number of possible triangles in it?
a. 10
b. 20
c. 30
d. 40
Answer: a. 10
Q5. Which of the following triangles are unstable?
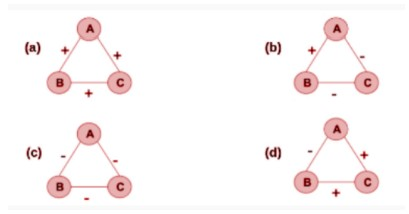
a. a and b
b. b and c
c. c and d
d. a and d
Answer: c. c and d
Q6. Can we have a complete signed graph on 4 nodes (K4) and 5 nodes (K5) respectively, each having exactly one unstable triangle respectively?
a. No, No
b. No, Yes
c. Yes, No
d. Yes, Yes
Answer: a. No, No
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q7. Select all that is True for a structurally balanced network according to the Balance theorem?
a. It can be a network with all positive relationships
b. It can be a network of two clusters with all positive relationships across and all negative relationships within cluster
c. It can be a network of two clusters with all positive relationships within and all negative relationships across cluster
d. It can be a network with all negative relationships
Answer: a, c
Q8. Given an unstable triangle with edges (+, +, −), this tends to become stable by transforming to a stable state. Which one of the following is an invalid option for such a stable state?
a. (+, +, +)
b. (+, −, −)
c. (−, −, +)
d. (−, −, −)
Answer: d. (−, −, −)
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q9. A friend’s friend tends to become a friend, and so does an enemy’s enemy. Pick out the reason(s).
a. Triadic closure
b. Structural balance
c. Social influence
d. Selection
Answer: a, b
Q10. When is a signed triangle said to be unstable?
a. zero positive edge
b. one positive edge
c. two positive edges
d. all positive edges
Answer: a, c
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
More Solutions of Social Networks: Click Here
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers/
Session: JULY-DEC 2023
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q1. Two people meet at a Health Club and then became friends with each other this represents
Triadic Closure
Membership closure
Focal closure
selection closure
Answer: Focal closure
Q2. Similarity measure can be defined as
Total number of work done by number of work in common
Number of work they do in common by Total Number of work done by both
Total number of friends by number of friends in common
Number of friends in common by Total Number of friends
Answer: Number of work they do in common by Total Number of work done by both
Q3. Social affiliation network is
Complete and bipartite
Complete and not bipartite
Bipartite and not Complete
Neither complete nor Bipartite
Answer: Bipartite and not Complete
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q4. In general, when we calculate the value for homophily it represents value between 0 to 1, what value will we get if it shows heterogeneity?
0
1
< 1
> 1
Answer: < 1
Q5. It is the tendency in which people make friends with similar interests i.e people select other people having similar habits or interests.
Homophily
Heterogeneity
Social Influence
Selection
Answer: Selection
Q6. If suppose A and B have 10 friends in common, and there is scenario that each common friend gives A and B an independent probability of 0.08 of forming a link. What is the probability that there exist a link between A and B?
1 − (0.92)^10
1 − (0.08)^10
0.9210
0.0810
Answer: 1 − (0.92)^10
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q7. Given a complete graph with 10 vertices the total number of possible triangle for the given graph will be
10000
30
300
120
Answer: 120
Q8. Which situation doesn’t occur when homophily in a network of 2 Classes is greater than 0.5?
Across edges are low in proportion
People tend to make friends within their group
The probability of selecting across edge is low
People make friends outside the group
Answer: People make friends outside the group
Q9. Which phenomenon is represented in region A of the graph in Figure 7 below?
Social Influence
Foci closure
Membership closure
Selection
Answer: Selection
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
Q10. Which phenomenon is represented in region B of the graph in Figure 7 below?
Social Influence
Foci closure
Membership closure
Selection
Answer: Social Influence
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 5 Assignment 5 Answers
More Weeks of Social Networks: Click here
More Nptel Courses: Click here
