Social Networks Week 4 Nptel Assignment Answers
Table of Contents
Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers (Jan-Apr 2025)
Q1. Granovetter’s theory of tie strength suggests that:
a) Strong ties contribute to the spread of new information across a network.
b) Weak ties act as bridges connecting different social clusters.
c) Passive engagement is the primary driver of tie formation.
d) Weak ties are more emotionally intense than strong ties.
Q2. In analyzing passive engagement on social media, which metric best captures a user’s interaction level?
a) Frequency of likes and comments
b) Time spent scrolling without explicit interaction
c) Number of posts shared per day
d) Ratio of followers to following
Q3. The betweenness centrality of a node v in a graph G is calculated by:
a) ∑i≠jσij(v)/σij, where σij is the total number of shortest paths between i and j, and σij(v) is the number of those paths passing through v.
b) The ratio of the node’s degree to the total number of edges.
c) The clustering coefficient of the node.
d) The sum of weights of edges connected to v.
Q4. In graph partitioning, the modularity measure is used to evaluate:
a) The density of a node’s local neighborhood.
b) The quality of a partition based on the ratio of intra-cluster and inter-cluster edges.
c) The average degree of nodes in a graph.
d) The overall size of the graph.
Q5. In a social network graph, strong relationships can be identified using:
a) Nodes with the highest degree centrality.
b) Nodes connected by edges with high weights representing frequent interactions.
c) Nodes with low clustering coefficients.
d) Nodes that are part of disjoint communities.
Q6. Weak relationships are considered essential in network analysis because:
a) They reduce the clustering coefficient of the network.
b) They enable diffusion of novel information between clusters.
c) They increase the density of the graph.
d) They are more stable than strong ties.
Q7. The homophily index measures the tendency of individuals to associate with similar others. It is mathematically represented as:
a) H = Number of similar connections / Total connections
b) H = Clustering coefficient / Degree centrality
c) H = Betweenness centrality × Degree centrality
d) H = Number of inter-group connections / Total connections
Q8. How can social influence be empirically tested in a longitudinal study of social networks?
a) By measuring changes in individuals’ behaviors after new connections are formed.
b) By calculating clustering coefficients of influential nodes.
c) By evaluating the modularity of the network before and after interventions.
d) By comparing the degree centrality of nodes over time.
Q9. Foci closure in social networks is strongly tied to:
a) Shared affiliation to activities or spaces that increase the likelihood of interaction
b) Strong ties that persist despite geographic separation.
c) Nodes with high betweenness centrality influencing smaller clusters.
d) The probability of network rewiring events.
Q10. The Fatman Evolutionary Model suggests preferential attachment in networks is driven by:
a) The degree of existing nodes and the relative fitness of new nodes.
b) Randomized connections that optimize modularity.
c) Shortest path distribution across clusters.
d) Edge weights that decay exponentially over time.
Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers (JULY-DEC 2023)
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q1. Two people meet at a Health Club and then became friends with each other this represents
Triadic Closure
Membership closure
Focal closure
selection closure
Answer: Focal closure
Q2. Similarity measure can be defined as
Total number of work done by number of work in common
Number of work they do in common by Total Number of work done by both
Total number of friends by number of friends in common
Number of friends in common by Total Number of friends
Answer: Number of work they do in common by Total Number of work done by both
Q3. Social affiliation network is
Complete and bipartite
Complete and not bipartite
Bipartite and not Complete
Neither complete nor Bipartite
Answer: Bipartite and not Complete
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q4. In general, when we calculate the value for homophily it represents value between 0 to 1, what value will we get if it shows heterogeneity?
0
1
< 1
> 1
Answer: < 1
Q5. It is the tendency in which people make friends with similar interests i.e people select other people having similar habits or interests.
Homophily
Heterogeneity
Social Influence
Selection
Answer: Selection
Q6. If suppose A and B have 10 friends in common, and there is scenario that each common friend gives A and B an independent probability of 0.08 of forming a link. What is the probability that there exist a link between A and B?
1 − (0.92)^10
1 − (0.08)^10
0.9210
0.0810
Answer: 1 − (0.92)^10
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q7. Given a complete graph with 10 vertices the total number of possible triangle for the given graph will be
10000
30
300
120
Answer: 120
Q8. Which situation doesn’t occur when homophily in a network of 2 Classes is greater than 0.5?
Across edges are low in proportion
People tend to make friends within their group
The probability of selecting across edge is low
People make friends outside the group
Answer: People make friends outside the group
Q9. Which phenomenon is represented in region A of the graph in Figure 7 below?
Social Influence
Foci closure
Membership closure
Selection
Answer: Selection
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q10. Which phenomenon is represented in region B of the graph in Figure 7 below?
Social Influence
Foci closure
Membership closure
Selection
Answer: Social Influence
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
More Weeks of Social Networks: Click here
More Nptel Courses: Click here
Session: JAN-APR 2023
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q1. Identify the type of Homophily in the following Linked inn recommendation:
”People with similar interests are following —-”
a. Selection
b. Social Influence
c. Membership closure
d. Foci Closure
Answer: a. Selection
Q2. Identify the network mechanism in play for the following transformation.
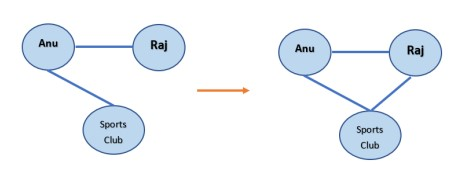
a. Triadic closure
b. Focal Closure
c. Membership closure
d. Neighborhood overlap
Answer: c. Membership closure
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q3. Two friends Raj and Nila have taken different courses according to their interests. Raj has completed 12 courses and Nila has completed 16 courses in all. There are 7 courses that Raj and Nila have taken up in common. What is the similarity measure for Raj and Nila?
a. 1/3
b. 7/28
c. 3
d. 28/7
Answer: a. 1/3
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q4. Suppose Manisha and Simran have a common friend with an independent probability p What is the probability that they donot have k common friends?
a. p×k
b. pk
c. (1−p)k
d. (1−(1−p))k
Answer: c. (1−p)k
Q5. What are the factors that influence the dynamics of friendships formation and behaviour of people in a network?
a. Social Influence
b. Selection
c. Both Social Influence and Selection
d. Neither Social Influence nor Selection
Answer: c. Both Social Influence and Selection
Q6. In the fatman evolutionary model, what is the role of social foci?
a. Selection
b. Social Influence
c. Both Social Influence and Selection
d. Neither Social Influence nor Selection
Answer: b. Social Influence
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q7. Compute Homophily for the given network.
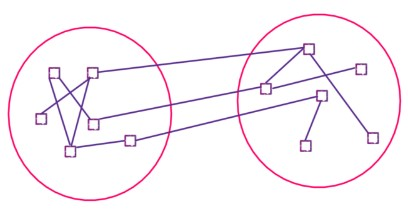
a. 1
b. 3/4
c. 1/2
d. 1/4
Answer: c. 1/2
Q8. What is the relationship that exists between the probability of any two persons(A and B) being friends with respect to the number of their common friends?
a. inverse
b. linear
c. polynomial
d. exponential
Answer: b. linear
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
Q9. A network having inter-community edge density and intra-community edge sparsity will definitely exhibit
a. Triadic closure
b. Selection
c. Homophily
d. Heterophily
Answer: d. Heterophily
Q10. Assume there are 20 participants who have just enrolled for a workshop. Which of the following closure happen in this current state?
a. Triadic closure
b. Membership closure
c. Focal closure
d. None
Answer: c. Focal closure
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 4 Assignment 4 Answers
More Solutions of Social Networks: Click Here
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers/
