Social Networks Week 2 Nptel Assignment Answers
Are you looking for AI in Marketing Nptel Week 2 Assignment Answers ? You are here at right place for answers solved by our experts at Progiez.
Table of Contents

Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment Answers (Jan-Apr 2026)
Que1. Ingredients like salt and oil having a large number of connections primarily indicates:
a) High clustering within a single cuisine
b) Frequent co-occurrence across many recipes
c) Strong bridging between distant clusters
d) Low overall influence
Que2. An ingredient with relatively few connections but crucial links between cuisine clusters is most significant because it:
a) Appears rarely
b) Forms tightly-knit local groups
c) Connects otherwise separate regions of the network
d) Reduces the size of clusters
Que3. The presence of tightly connected ingredient groups suggests that:
a) Recipes are uniformly distributed
b) Ingredients combine randomly
c) Certain cuisines form dense substructures
d) All ingredients serve the same role
Que4. Which analysis would best help identify substitute ingredients within this network?
a) Counting total appearances
b) Finding ingredients within the same dense clusters
c) Measuring shortest paths across the entire network
d) Removing highly connected ingredients
Que5. The overall structure of the ingredient network most closely reflects a system where:
a) Most nodes have similar connectivity
b) A few nodes dominate connections while many remain peripheral
c) Nodes form a strict hierarchy
d) Connections grow linearly
Case Study 2 : Analyzing Influence and Structure in a Large-Scale Synonym Network
Que6. Words like good having many synonym connections would most directly result in high values of:
a) Clustering coefficient
b) Degree centrality
c) Network diameter
d) Path length
Que7. A word with low degree but appearing on many shortest paths is important primarily because it:
a) Appears frequently in text
b) Belongs to a dense cluster
c) Connects different groups of words
d) Has high clustering
Que8. The fact that removing a few words caused the network to break apart suggests those words had:
a) High PageRank
b) High betweenness
c) High clustering
d) Low degree
Que9. Which NetworkX operation would best help identify groups of words with similar meanings?
a) Shortest path computation
b) Community detection
c) Degree sorting
d) BFS traversal
Que10. A degree distribution where many nodes have small degree and few have very large degree suggests:
a) Uniform structure
b) Random network
c) Presence of hubs
d) Tree-like structure
Case Study 3 : Tracking Influence and Visibility in the Web Graph
Que11. A webpage receiving links from already influential pages gains higher visibility mainly because PageRank considers:
a) Total number of users
b) Number of outgoing links
c) Quality of incoming links
d) Age of the webpage
Que12. Pages with no outgoing links require special handling because they:
a) Reduce network size
b) Absorb rank without redistributing it
c) Increase clustering
d) Break directed paths
Que13. Compared to simple link counting, PageRank provides better results because it:
a) Ignores direction of links
b) Treats all links equally
c) Considers influence of linking pages
d) Penalizes popular pages
Que14. Which modification is most likely to improve a webpage’s PageRank score?
a) Adding self-links
b) Getting links from authoritative sites
c) Removing all outgoing links
d) Increasing page size
Que15. The overall structure of the web graph most closely resembles:
a) Tree
b) Undirected random graph
c) Directed network with hubs
d) Complete graph
Question 1. Which of the following could be used as an indicator of a central ingredient in the Ingredients Network?
a) High degree centrality
b) Low clustering coefficient
c) High betweenness centrality
d) Minimum spanning tree membership
Question 2. If the network is unweighted and undirected, which metric would best indicate an ingredient that connects various ingredient clusters?
a) Degree centrality
b) Betweenness centrality
c) PageRank
d) Closeness centrality
Question 3. Which of the following actions might increase the clustering coefficient of a node representing an ingredient?
a) Adding edges among its neighbors
b) Using it in recipes that already share many other ingredients
c) Decreasing its degree
d) Connecting it to an isolated node
Question 4. What is the best way to identify substitute ingredients in the network?
a) Using PageRank
b) Using community detection to find clusters of similar-use ingredients
c) Finding the node with maximum degree
d) Running BFS from each node
Question 5. Ingredients with high clustering coefficient are likely to:
a) Appear in tightly-knit groups of recipes
b) Be used rarely
c) Be part of cultural or cuisine-specific subgroups
d) Form bridges between disparate recipes
Question 6. The network of ingredients is most similar in structure to which type of network?
a) Tree
b) Star
c) Small-world network
d) Linear chain
Question 7. What graph property makes a word like “good” a hub?
a) High degree
b) High centrality
c) Low clustering coefficient
d) High eigenvector falloff
Question 8. What type of network model is most appropriate for modeling the synonymy network?
a) Tree
b) Undirected unweighted graph
c) Directed weighted graph
d) Bipartite graph
Question 9. Why might peripheral nodes in the synonym network be important?
a) They add richness to language use
b) They might connect rarely used synonym groups
c) They have highest centrality
d) They always form cycles
Question 10. What kind of analysis can help group together words with similar meanings?
a) DFS traversal
b) Community detection
c) Shortest path algorithm
d) Bipartite projection
Question 11. In the synonymy network, a node with low degree but high betweenness might indicate:
a) A bridge between two different meaning clusters
b) A context-specific synonym
c) A very frequent word
d) An isolated component
Question 12. What type of network metric can help identify formal vs informal word usage patterns?
a) PageRank
b) Clustering within sociolect subgraphs
c) Tree depth
d) Diameter of network
Question 13. PageRank is influenced by:
a) Number of incoming links
b) Quality (PageRank) of linking pages
c) Number of outgoing links
d) Number of total users
Question 14. A page with many incoming links from low-ranked pages is likely to:
a) Have very high PageRank
b) Never rank at all
c) Have modest PageRank depending on damping factor
d) Break the algorithm
Question 15. In the web graph, a dangling node is:
a) A node with no outgoing links
b) A node with no incoming links
c) A broken hyperlink
d) A self-looped node
Question 16. Which graph algorithm is most appropriate to identify top influencers in the web graph?
a) Dijkstra’s algorithm
b) PageRank
c) BFS
d) Kruskal’s algorithm
Question 17. Which of these changes could improve a site’s PageRank?
a) Getting linked from authoritative websites
b) Reducing number of outbound links on important pages
c) Removing internal links
d) Adding self-loops
Question 18. The Web Graph most resembles:
a) Undirected graph
b) Balanced binary tree
c) Bipartite graph
d) Directed scale-free network
Question 19. Which Python libraries are best suited for analyzing such social network graphs?
a) NetworkX
b) Pandas (for data preprocessing)
c) TensorFlow
d) Seaborn
Question 20. What metric would best identify a user who connects disparate groups?
a) Closeness centrality
b) Betweenness centrality
c) Degree centrality
d) Eigenvector centrality
Question 21. Community detection can help:
a) Identify social circles
b) Predict content spread boundaries
c) Compute path lengths
d) Rank friends
Question 22. A tightly-knit group of users with many mutual friends is likely to form:
a) A PageRank cluster
b) A path component
c) A community
d) A bipartite set
Question 23. Which of these plots would be helpful in visualizing the degree distribution?
a) Histogram
b) Log-log plot
c) Heatmap
d) Confusion matrix
Question 24. What does a power-law distribution in degree typically suggest?
a) Uniform connectivity
b) Presence of hubs
c) Graph is bipartite
d) Random structure
Question 25. The sudden emergence of a giant connected component is an example of:
a) Phase transition in networks
b) Percolation theory in action
c) Clique formation
d) Graph diameter reduction
Question 26. As new edges are added randomly, when is a giant component most likely to emerge?
a) After adding 10% of edges
b) Near the critical threshold in Erdős–Rényi model
c) Immediately
d) When all nodes have same degree
Question 27. Factors influencing the rate of connectedness emergence include:
a) Average degree
b) Number of nodes
c) Time of day
d) Color of nodes
Question 28. Which real-world phenomenon reflects the same principle?
a) A virus mutating
b) A trending hashtag
c) A viral video suddenly reaching millions
d) Blockchain mining
Question 29. Which of these methods can detect when a giant component has formed?
a) Analyzing component sizes over time
b) Checking network diameter
c) BFS from random node
d) Comparing node colors
Question 30. In graph theory, a component is:
a) A central node
b) A directed edge
c) A maximal connected subgraph
d) A subgraph with cycles only
Question 31. Which of the following network properties would best identify influential contributors?
a) High in-degree (number of incoming replies/comments)
b) High eigenvector centrality
c) Low clustering coefficient
d) Membership in isolated components
Question 32. Which metric would help detect tightly-knit learning groups?
a) Degree centrality
b) Clustering coefficient
c) PageRank
d) Edge betweenness
Question 33. A user with high betweenness centrality is likely to:
a) Connect different learning communities
b) Facilitate knowledge transfer between groups
c) Be isolated from core discussions
d) Have the most followers
Question 34. Which algorithm is most suitable for identifying natural study groups in the network?
a) BFS
b) Dijkstra’s algorithm
c) Community detection (e.g., Girvan–Newman or Louvain)
d) Kruskal’s algorithm
Question 35. Factors contributing to strong collaborative ties may include:
a) Frequent co-participation in threads
b) Repeated peer review or feedback
c) Random logins
d) Degree of anonymity
Question 36. In such a learning network, a node with high closeness centrality can:
a) Disseminate information quickly to the whole network
b) Only influence its direct neighbors
c) Be easily removed without effect
d) Belong to disconnected components
1. A graph has a diameter of 1. Which of the following statements must be true?
(a) The graph is a complete graph.
(b) All nodes in the graph are directly connected to every other node.
(c) The graph contains the maximum possible number of edges for its number of nodes.
(d) The graph is sparse with relatively fewer edges compared to nodes.
(e) Adding or removing an edge cannot change its diameter.
2. In the Web Graph model, what do the nodes and edges represent?
(a) Nodes are web pages, and edges are hyperlinks between them.
(b) Nodes are servers, and edges are data transfer rates.
(c) Nodes are users, and edges are user interactions.
(d) Nodes are hashtags, and edges are co-occurrence frequencies.
3. A dataset represents a multigraph (a graph where multiple edges are allowed between two nodes). Which method in NetworkX allows you to load such a graph from an edge list file?
(a) read_multiedgelist()
(b) read_edgelist() with create_using=nx.MultiGraph()
(c) read_gml()
(d) read_multigraph()
4. Consider the following GML representation of a directed graph.

Which of the following correctly interprets the structure and properties of the graph described by the GML code?
(a) The graph is undirected, with two nodes labeled “A” and “B” connected by two edges with weights 5 and 3, respectively.
(b) The graph is directed, with node “A” pointing to node “B” with a weight of 5, and node “B” pointing back to node “A” with a weight of 3.
(c) The graph is directed, with node “A” pointing to node “B” with a weight of 3, and node “B” pointing to node “A” with a weight of 5.
(d) The graph is directed and contains a self-loop at node “A” with a weight of 5, and another self-loop at node “B” with a weight of 3.
5. Consider the following characteristics of different social network dataset formats. Which of the following statements is true about these formats?
(a) Adjacency Matrix is most efficient for storing sparse graphs because it requires minimal space for large graphs with few edges.
(b) Edge List format is not ideal for storing sparse graphs as it does not require extra space to store non-existing edges between nodes.
(c) Adjacency List is space-efficient for sparse graphs and allows for fast traversal of neighbors, making it suitable for networks with relatively few edges compared to nodes.
(d) Gephi File format is designed for large-scale networks and is not ideal for visualizing or analyzing graphs with edge weights or node attributes.
6. Pajek datasets are usually available in which of the following formats?
(a) .csv
(b) .net
(c) .tar
(d) .txt
7. Which NetworkX function would you use to visualize the degree distribution of a graph?
(a) nx.degree_histogram(G)
(b) nx.closeness_centrality(G)
(c) nx.eigenvector_centrality(G)
8. In Gephi, which metric would you compute to determine the connectivity between communities in a graph?
(a) Modularity
(b) Degree centrality
(c) Closeness centrality
(d) Betweenness centrality
9. In the context of graph theory, what is the critical threshold for the emergence of a giant connected component in a random graph?
(a) When the number of edges equals the number of nodes.
(b) When the average degree is 1.
(c) When the clustering coefficient reaches 1.
(d) When the network diameter becomes constant.
10. In a random graph, when does a giant connected component typically emerge?
(a) When the edge probability p is very small.
(b) When the edge probability p is large enough to connect most nodes.
(c) When the number of nodes n is very large.
(d) When the graph has no isolated nodes.
Q1. Find the diameter for the given graph G in Figure 1
3
4
5
6
Answer: 4
Q2. Which of the following networks is a directed graph?
followers on instagram account
facebook friendship network
collaboration network
ingredients network
Answer: followers on instagram account
Q3. What will be the range of clustering coefficient for any vertex in undirected graph with no loop and multiple edges?
0 to 1
0 to infinity
-infinity to infinity
-1 to +1
Answer: 0 to 1
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q4. Key tag in GraphML is used to assign
Node only
Edge only
Both node and edge
loop
Answer: Both node and edge
Q5. Expand GEXF.
Graphical Extension XML Format
Graphx Extension XML Format
Graph Exchange XML Format
Graph Extend Exchange Format
Answer: Graph Exchange XML Format
Q6. Compute density of the given graph.
0
1/2
1/3
1/4
Answer: 1/3
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q7. For the given graph H in Question 6, If A=highestdegree∑ degree, what will be the value of A?
1
1/2
1/5
2/5
Answer: 1/2
Q8. Choose the data set format which starts with the keyword “graph”?
GML
Graph Exchange XML
txt
GEXF
Answer: GML
Q9. The degree distribution of most real-world networks follows which law?
Zipf’s Law
Benford’s Law
Power Law
Difficult to say; can follow any distribution
Answer: Power Law
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q10. Pick out the clustering coefficient for Node A in the given graph K.
1/6
3/4
1/3
1/2
Answer: 1/6
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
More Weeks of Social Networks: Click here
More Nptel Courses: Click here
Session: JAN-APR 2023
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q1. Consider the ingredient network where a node represents an ingredient and an edge exists between two nodes if there is a dish where both the ingredients are used. Which of the following statements is true for the nodes of the same community in such a network?
a. ingredients that are often used together
b. ingredients that are never used together
c. ingredients that are rarely used together
d. none of the above
Answer: a. ingredients that are often used together
Q2. For the Synonymy network, the path from Love to Hatred is because
a. Both are synonymous
b. both the words are connected by anonymous words
c. of degradation of synonymity along the path
d. mistake in edges connecting them
Answer: c. of degradation of synonymity along the path
Q3. Identify the network that is a Directed graph.
a. Friendship network
b. Email network
c. Road network
d. Co-authorship network
Answer: b. Email network
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q4. Which of the following statements is True for GML format of networks?
Statement I: Labels and attributes can be added
Statement II: Weights cannot be added
a. Only I
b. Only II
c. Both I and II
d. Neither I nor II
Answer: a. Only I
Q5. The degree distribution of most real world datasets follows
a. Law of large numbers
b. Power law
c. Universal law of Approximation
d. Benford’s law
Answer: b. Power law
Q6. Given a complete graph with 99 nodes, what is the average clustering coefficient?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 0.5
d. 0.25
Answer: b. 1
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q7. What is the diameter of Graph G?
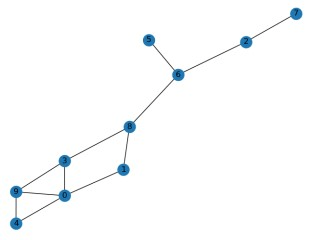
a. 5
b. 6
c. 7
d. 8
Answer: b. 6
Q8. Calculate the clustering coefficient of vertex ’0’ in the following graph H.
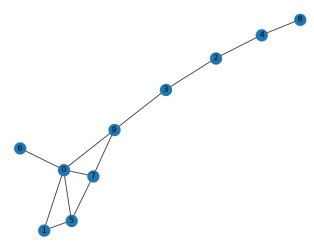
a. 0.1
b. 0.2
c. 0.3
d. 0.4
Answer: c. 0.3
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
Q9. Given n nodes, what is the minimum number of edges required to make the graph connected?
a. O(logn)
b. O(n2)
c. O(n3)
d. O(nlogn)
Answer: d. O(nlogn)
Q10. Calculate the density of the following graph
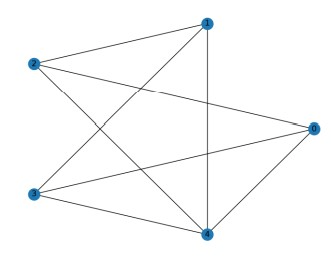
Answer: 0.80
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 2 Assignment 2 Answers
More Solutions of Social Networks: Click Here
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers/