An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence | Week 8
Session: JAN-APR 2024
Course name: An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Course Link: Click Here
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q1. Consider the given joint distribution
Calculate the value of P(cavity | ¬ toothache) + P(cavity | catch).
Round the answer up to 2 decimal places. (e.g., if the answer is 0.1372, return 0.14)
Answer: 0.63
Q2. There are 1000 coins — 999 are fair, and 1 has heads on both sides. You randomly choose a coin and flip it 10 times. Miraculously, all 10 flips turn up heads. What is the probability that you chose the unfair coin? If the answer is of the form m/n, where m and n are relatively co-prime, return m+n.
Answer: 3047.0
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q3. Which of the following statements is/are true?
X is conditionally independent of B given A, D, and F.
X is conditionally independent of F given A.
X is conditionally independent of D given A.
X is conditionally independent of F given D.
Answer: a), b)
Q4. Compute P(A = true | X = true, B = false), given that
P(A = true) = 0.4, P(X = true | A = true) = 0.3, P(X = true | A = false) = 0.2, P(B = true | A = true) = 0.5, P(B = true | A = false) = 0.4
Return the answer (rounded) up to 2 decimal places.
Answer: 0.45
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q5. What is the minimum number of parameters needed to store the full joint distribution?
Answer: 14
Q6. Which of the following is/are true ?
Any boolean formula can be converted to a Bayesian Network, performing inference on which can tell us how many models satisfy the original boolean formula
Exact Inference for a general Bayes Net is NP-Hard
Exact Inference for certain kind of Bayes Nets can be done in polynomial time
Approximate inference can be done for Bayes Nets using sampling in polynomial time
Answer: a), b), c), d)
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q7. Which of the following is/are true for a Bayes Network ?
Bayesian Network (structures) are Directed Acyclic Graphs
There exists a unique bayesian network for a given joint probability distribution
Bayes Networks encode conditional independence relations between variables and can often compactly represent a joint probability distribution.
For any Bayes Network, a variable is conditionally independent of all other variables given all its parents
Answer: a), c)
Q8. We are given the following Bayes Network (as discussed in the videos)
How many of the following statements are true ?
i. Earthquake and Burglary are independent of each other
ii. Given Alarm, Burglary is independent of Earthquake
iii. Given Alarm, JohnCalls and MaryCalls are independent of each other
iv. JohnCalls and MaryCalls are independent of Each other
v. Given Earthquake and Burglary, Alarm is independent of MaryCalls and JohnCalls
vi. JohnCalls is dependent of Burglary given Earthquake
vii. Given Alarm, JohnCalls is independent of all other variables
viii. Given Alarm, Burglary is independent of both JohnCalls and MaryCalls
Answer: 5
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q9. In the Bayesian Network given below, what is the probability that Mary calls given that an Earthquake has occurred and a burglary has not taken place?
Write the solution rounded to 4 decimal places
Answer: 0.2101
Q10. In the same Bayesian Network given below, what is the probability that Mary calls given that an Earthquake has occurred?
Write the solution after rounding off to first 4 decimal digits.
Answer: 0.2106
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
More Weeks of An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence: Click here
More Nptel Courses: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers
Course Name: An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Course Link: Click Here
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
For Question 1 to 3 –
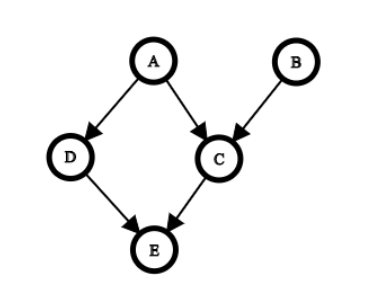
Q1. Minimum number of values required to store the above Bayes net is
Answer: 12
Q2. Which of the following are true about the above bayesian network?
a. C is conditionally independent of D, given A.
b. C is conditionally independent of D, given E.
c. B is conditionally independent of A, given C.
d. B is conditionally independent of C, given A
Answer: a. C is conditionally independent of D, given A.
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q3. Given C and D, E is independent of which of the following variables? (Select only one option)
a. A
b. B
c. Both A and B
d. Neither A nor B
Answer: c. Both A and B
Q4. Which of the following statements are true?
a. Bayesian network can be used to find the number of satisfying assignments for any Boolean formula
b. Inference in a Bayesian network always has exponential time complexity, irrespective of structure
c. Inference in a Bayesian network may be polynomial time for certain structures of the network
d. Cut sets can simplify inference in Bayesian networks
Answer: a, c, d
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q5. Which of the following will always hold?
a. P(a,b) = P(a|b)P(b)
b. P(a,b|c) = P(a|c)P(b|c)
c. 1 = P(a|¬b) + P(a|b)
d. P(a,b|c) = P(b|c)P(a|b,c)
Answer: a, d
Q6. Consider the following Bayesian network along with the conditional probabilities given below. What is the value of P(C | D,E)? Give the answer as a decimal rounded to 2 decimal places (for example, 0.12 for 0.1234)
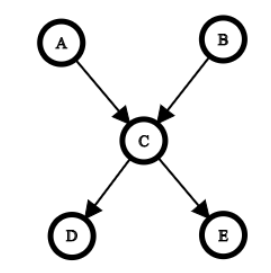
P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.4, P(C| A,B) = 0.9, P(C| ¬A,B) = 0.5, P(C| A,¬B) = 0.2, P(C| ¬A,¬B) = 0.1, P(D | C) = 0.8, P(D| ¬C) = 0.2, P(E | C) = 0.1, P(E | ¬C) = 0.4.
Answer: 0.37
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q7. In the above question, which are the evidence and hidden variables for the computation of P(C | D,E)? Return the answer as evidence variables followed by hidden variables separated by a %, where each group is lexicographically sorted (eg. if evidence is C and D and hidden variable is A, return CD%A).
Answer: DE%AB
Q8. Consider the following joint probability matrix. Each row contains a value for x and each column contains a value for y. What is the value of P(y=2|x=2)? Give the answer as a decimal rounded to 2 decimal places (for example, 0.12 for 0.123)
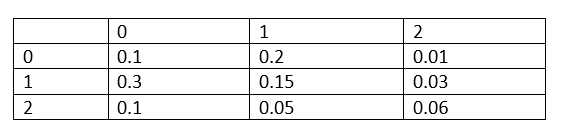
Answer: 0.29
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q9. You toss a fair coin 3 times. Given that you observed at least one head, what is the probability that you observed at least 2 heads? If the answer is expressed as m/n where m and n are coprime, give the answer as m+n.
Answer: 11
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
Q10. Which of the following statements are correct?
a. There exists a unique Bayesian network for every joint probability distribution.
b. Multiple valid Bayesian networks can be constructed to represent the same joint probability distributions.
c. Two variables in a bayesian network are conditionally independent if and only if they are d-separated.
d. Bayesian network structures are required to be directed acyclic graphs.
Answer: b, d
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 8
More Solutions of An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence: Click Here
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers/
