An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence | Week 2
Session: JAN-APR 2024
Course name: Leadership and Team Effectiveness
Course Link: Click Here
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q1. Consider the Vacuum World Illustration as covered in the videos. Assume that now there are 3 rooms and 2 Roombas (autonomous robotic vacuum cleaners). Each room can be either dirty/clean and each Roomba is present in one of the 3 rooms.
What are the number of states in propositional/factored knowledge representation?
Answer: 72
Q2. Which of the following is/are part of a node?
State
Path cost from initial state
Path cost to the goal
Parent node
Answer: a, b, d
State
Path cost from initial state
Parent node
Q3. Full duplicate detection can reduce the number of nodes to be visited from exponential to linear (in problem size).
True
False
Answer: True
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
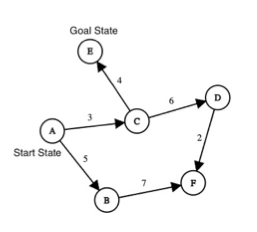
Q4. Start from state A. Goal state is G. The number over each edge indicates the cost to transition from one state to another. What is the order of nodes visited by BFS (including the start and goal state too)? Break any ties using lexicographic ordering and do not perform duplicate detection.
Answer: ABCDEFFG
Q5. Start from state A. Goal state is G. The number over each edge indicates the cost to transition from one state to another. What is the cost of the path given by BFS? Break any ties using lexicographic ordering and do not perform duplicate detection.
Answer: 24
Q6. Consider the given graph.
What is the order of nodes visited by IDDFS (Iterative-deepening depth-first search)? Start from A, Goal State is E, break any ties using lexicographic ordering, and no duplicate detection.
Answer: AABCABFCDE
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q7. Which of the following problems is typically not modelled as a search problem?
Puzzle Solving eg. solving the 8-Puzzle
Path finding eg. finding the shortest path to a hospital in your city starting from your home
Stock Market Prediction i.e. predicting the stock prices using historical data / trends
Path Planning eg. finding the minimum cost path that visits all nodes in a graph and returns to the source node
Answer: Stock Market Prediction i.e. predicting the stock prices using historical data / trends
Q8. Which of the following is/are true for a search tree with a finite branching factor and all costs greater than one?
Depth-First Search (DFS) is not complete
Iterative Deepening Search is systematic
Uniform Cost Search is optimal
Breadth-First Search is typically preferred over Depth-First Search in situations where memory is limited
Answer: a, c
Depth-First Search (DFS) is not complete
Uniform Cost Search is optimal
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q9. Suppose there is only one goal state and each step cost is k (k>0, k is constant). Which of the following search algorithm(s) will return the optimal path?
Breadth-First Search
Depth First Search
Uniform Cost Search
Iterative Deepening Search
Answer: Breadth-First Search
Uniform Cost Search
Iterative Deepening Search
Q10. Which of the following is/are false regarding search? The maximum branching factor of the search tree is finite and is represented by b, d is the depth of the least cost solution and m is the maximum depth of the search-space
If m >> d, DFS (depth-first search) has a better worst-case time complexity than BFS (breadth-first search)
Unlike Iterative Deepening Search, BFS visits each world state exactly once and has a better worst-case time complexity than iterative deepening search
Bidirectional search, if applicable, has a better worst-case space complexity than BFS
BFS is optimal even if all step costs are not identical
Answer: a, b, d
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
More Weeks of An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence: Click here
More Nptel Courses: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers
Course Name: An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
Course Link: Click Here
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q1. Consider the “Vacuum World” discussed in the lecture. The state space of the problem is shown below.
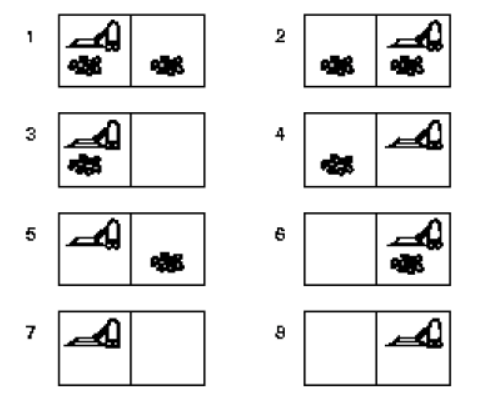
We have two possible actions: moving the vacuum cleaner from one room to another (cost = 2 units) and clean the current room using the vacuum cleaner (cost = 1 unit). What is the minimum cost required to clean all the dirt, assuming we start in state 1?
a. 8
b. 6
c. 4
d. 5
Answer: c. 4
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q2. Consider the following graph with start state A and goal state J. Assume that edges between nodes have cost equal to the absolute difference of the position of the corresponding letters in the alphabet. For example, cost of the edge between state F and J is 4 since F is the 6th and J is 10th letter of the alphabet. Also, assume that all edges are bidirectional and ties are broken lexicographically.
What will be the total number of nodes visited by Uniform Cost Search (include the goal state in your calculation)?
Answer: 10
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
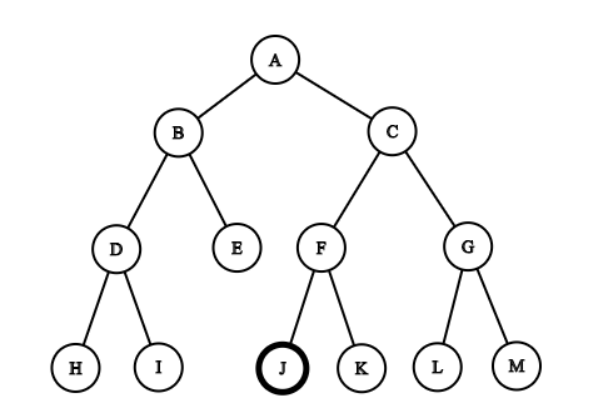
Q3. Consider the following graph. A is the initial state and we always pick the lexicographically smallest state in case of a tie. If the goal state is K, find the order of exploration of states in Breadth First Search with no duplicate checking. (Write the answer as a capitalized string with no spaces.
For example, if the order of exploration is A followed by B followed by C followed by D then write ABCD. Include the goal state in the answer)
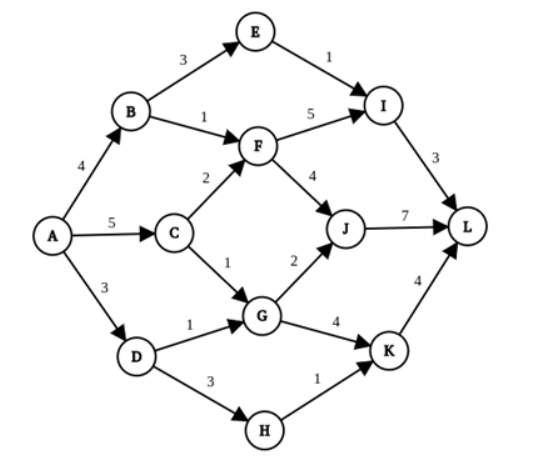
Answer: ABCDEFFGGHIIJIJJK
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q4. Which of the following types of state representations assume a state to be indivisible without any internal structure?
a. Atomic
b. Propositional
c. Relational
d. First-order
Answer: a. Atomic
Q5. Which of the following data structures are most suited to be used in an implementation of Breadth First Search (BFS) and Depth First Search (DFS)?
a. BFS: Queue, DFS: Queue
b. BFS: Queue, DFS: Stack
c. BFS: Stack, DFS: Queue
d. BFS: Stack, DFS: Stack
Answer: b. BFS: Queue, DFS: Stack
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q6. Which of the following search methods cannot be guaranteed to find a goal reaching plan to the 8-puzzle problem?
a. Bidirectional Search
b. Depth First Search
c. Breadth First Search
d. Beam Search
Answer: d. Beam Search
Q7. What is the best characterization of time and space complexity of Depth First Search with full duplicate detection (ensuring that the same state is never expanded again, b denotes maximum branching factor, m is maximum depth of search tree, d is the minimum depth of goal state and |S| is the total number of states, all of which are reachable from the start state)?
a. Time: O(bd) Space: O(bd)
b. Time: O(|S|) Space: O(|S|)
c. Time: O(bd) Space: O(bd)
d. Time: O(bm) Space: O(bm)
Answer: b. Time: O(|S|) Space: O(|S|)
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q8. Consider a variant of Iterative Deepening Depth First Search (IDS) in whichwe increase the depth in steps of 2, i.e. the depth limits increase as 1,3,5,7…. Which of the following is true about this new variant?
a. It is complete
b. It is optimal
c. It will always expand more nodes than standard IDS
d. It can find the goal state faster than IDS in some cases
Answer: a, d
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
Q9. Which of the following algorithms are optimal, complete and systematic for a search problem with a single goal state and same cost for all edges?
a. Breadth First Search
b. Bidirectional Breadth First Search
c. Iterative Deepening Depth First Search
d. Depth First Search
Answer: a, b
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
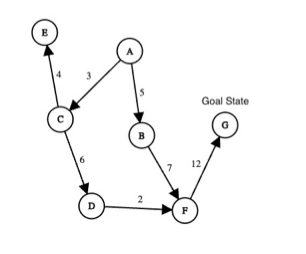
Q10. Consider the following graph in which we are searching from start state A to goal state G. The number over each edge is the transition cost. Find the path to the goal found by Depth First Search with full duplicate detection. In case of ties, the unvisited child with the lowest cost edge connecting it to the current node is selected. Further ties are broken with the lexicographically smaller state chosen.
(Write answer as a capitalized string with no spaces. For example, if the order of exploration is A followed by B followed by C followed by D then write ABCD. Include the goal state in the answer)
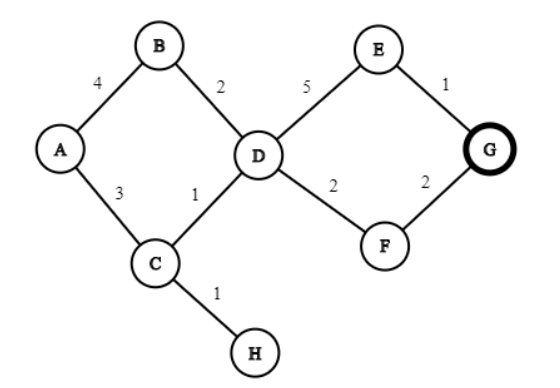
Answer: ACDFG
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
These are An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Answers Week 2
More Solutions of An Introduction to Artificial Intelligence: Click Here
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/answers/nptel/
