Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Are you looking for Nptel Social Networks Week 3 Assignment Answers ? You are here at right place for Week 3 assignment answers
Table of Contents

Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers (July-Dec 2025)
Question 1. According to Granovetter’s weak tie theory, which situation in this network is most likely to bring new information (like a job opportunity) to Alice?
a) Alice’s close colleague in the same team shares a tip
b) Alice learns of a job opening from a college acquaintance in another department
c) Alice reads about the job in an internal memo posted by HR
d) Alice’s mentor (her team leader) informs her directly
Question 2. In the company network, an edge between two employees has high embeddedness. What does this imply about their relationship?
a) They have many mutual friends, so they trust each other and can enforce norms
b) They are the only connection between their teams, acting as a bridge
c) They share no common contacts (neighborhood overlap 0)
d) They have completely different roles and no trust
Question 3. Alice acts as a liaison between the marketing and engineering teams, which are otherwise not directly connected. What network concept describes Alice’s advantage in this position?
a) Clique formation
b) Community detection
c) Structural hole (brokerage)
d) Triadic closure
Question 4. In this organizational network, an edge that is the only path connecting two distinct groups of employees (with no alternate route) is called a:
a) Strong tie
b) Local bridge
c) Cluster edge
d) Embedded tie
Question 5. In this context, which of the following statements about weak ties (Alice’s acquaintances) are correct?
a) They tend to be bridges between groups and are crucial for information flow.
b) They usually form redundant paths within a tightly knit team.
c) They provide access to novel information from outside Alice’s team.
d) They create high clustering (closed triads) in Alice’s local network.
Question 6. A friendship triad where each person is friends with the other two is called a:
a) Closed triad (triangle)
b) Structural hole
c) Local bridge
d) Open triad
Question 7. The local clustering coefficient of a student’s node measures:
a) How likely the student is to start a rumor
b) The proportion of the student’s friends who are also mutual friends with each other
c) The number of weak ties the student has
d) The number of communities the student belongs to
Question 8. If Dave has 4 friends, and among those friends there are 2 friendships between them, what is Dave’s local clustering coefficient?
a) 1/6
b) 1/3
c) 1/2
d) 1
Question 9. The neighbourhood overlap of an edge between two students X and Y is defined as the fraction of their friends they have in common. If X and Y share no mutual friends, their neighborhood overlap is 0, and that edge is a:
a) Local bridge
b) Closed triad
c) Strong tie
d) Embedded tie
Question 10. If Student Y shares 2 mutual friends with Student Z, and Y has degree 5 (including Z) and Z has degree 4 (including Y), the neighbourhood overlap is:
a) 1/2
b) 1/6
c) 1/4
d) 2/5
Question 11. An employee who connects many colleagues across different departments is likely to have increased:
a) Social capital by bridging structural holes
b) Network constraint and isolation
c) Clustering coefficient in their local network
d) Closed-loop redundancy
Question 12. In the Girvan–Newman community detection method, what is removed first to reveal communities?
a) Nodes with highest degree
b) Edges with highest betweenness centrality
c) Random edges until clusters form
d) Edges within dense subgroups
Question 13. The Girvan–Newman algorithm produces a hierarchy of communities in the form of a:
a) Single cluster
b) Dendrogram
c) Flat partition
d) Matrix of distances
Question 14. If Alice is a broker between two communities, what risk does she face according to social network theory?
a) Increased time/energy to maintain ties (trade-off)
b) Automatic promotion to a managerial position
c) Losing all her intra-community ties
d) Having a zero clustering coefficient
Question 15. Using the Girvan–Newman algorithm on a network with 20 employees, which approach does it use to determine community splits?
a) Checking all possible divisions (brute force)
b) Removing the lowest-weight edges first
c) Iteratively removing edges with highest between-group communication
d) Merging individuals into growing clusters until modularity peaks
Question 16. In the mobile phone network, if two users share a large number of common contacts (high neighbourhood overlap), what does Granovetter’s hypothesis predict about their call frequency?
a) They will have a very low call frequency.
b) They will likely have a high call frequency.
c) Neighborhood overlap has no relation to call frequency.
d) They will only communicate through intermediaries.
Question 17. Empirical findings from the mobile data suggest that edges with high weight (many calls) tend to have:
a) High overlap (many mutual contacts)
b) Zero overlap (no mutual contacts)
c) Always be local bridges
d) Be randomly distributed regardless of overlap
Question 18. In the call network, what kind of tie is expected to connect two loosely connected clusters of individuals?
a) A strong tie with high overlap
b) A weak tie with near-zero overlap
c) A repeated strong triadic tie
d) A triadic closure edge
Question 19. Researchers found that confirming Granovetter’s theory in mobile data indicates which of the following about weak ties in this network?
a) Weak ties were associated with high embeddedness.
b) Weak ties tended to span between different clusters.
c) Strong ties were never present.
d) Weak ties had no role in information diffusion.
Question 20. If two city residents have an overlap ratio Oij = 0.5 in their call network, which statement is true?
a) They share all their contacts in common.
b) They have half of their respective contacts in common (suggesting a fairly strong tie).
c) They share no contacts in common.
d) They do not communicate by phone.
Question 21. A brute-force community detection method:
a) Iteratively removes edges by centrality.
b) Tries every possible division of nodes into groups.
c) Merges nodes based on degree.
d) Uses edge overlap metrics only.
Question 22. The main drawback of brute-force methods compared to Girvan–Newman is:
a) They cannot find the optimal solution.
b) They run too quickly for large networks.
c) They are computationally expensive (exponential time).
d) They ignore edge weights.
Question 23. Girvan–Newman differs from brute-force in that it:
a) Seeks communities by maximizing the local clustering coefficient.
b) Recursively removes likely inter-community edges.
c) Randomly assigns nodes to communities.
d) Requires prior knowledge of the number of communities.
Question 24. In a small test network, both brute-force and Girvan–Newman find two communities of equal size. What advantage might Girvan–Newman have?
a) It guaranteed the globally best partition.
b) It is easier to explain by edge betweenness concept.
c) It provides a clear hierarchy (dendrogram).
d) It avoids calculating any centrality measures.
Question 25. Which statement is true about these two community detection approaches?
a) Brute-force always yields fewer communities than Girvan–Newman.
b) Girvan–Newman cannot handle weighted networks.
c) Brute-force exhaustively finds the best split by any criterion (e.g., intra/inter edge ratio).
d) Girvan–Newman is also brute-force in computing betweenness.
Question 26. A local bridge in this network is an edge whose endpoints have:
a) High neighborhood overlap (many mutual friends).
b) No mutual friends (neighborhood overlap 0).
c) Maximum betweenness centrality.
d) Been reinforced by multiple interactions.
Question 27. In terms of rumor propagation, edges with high embeddedness (many mutual neighbors) tend to:
a) Quickly spread rumors to new parts of the network.
b) Keep the rumor circulating within a local clique.
c) Stop the rumor entirely.
d) Always become local bridges.
Question 28. Which statement about rumors and weak ties is supported by network theory?
a) Rumors spread faster along edges with many mutual friends.
b) Bridges (weak ties) help the rumor jump between cliques.
c) Only strong ties carry rumors in a dense network.
d) Rumors cannot cross a local bridge.
Question 29. If student X has a friendship that is a local bridge to another cluster, X is likely:
a) Highly embedded in their own clique and also well-connected to the other clique.
b) Having no influence on rumor spread.
c) The sole connection point for the rumor to reach the other cluster.
d) Part of a complete triad with the other cluster.
Question 30. When a rumour starts in a dense clique, which tie is most critical for spreading it outside the clique?
a) Any strong tie within the clique.
b) Weak tie that is a local bridge to another clique.
c) The tie with the highest clustering coefficient.
d) A randomly chosen tie.
Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers (Jan-Apr 2025)
Course Link: Click Here
- Which of the following best explains the concept of strength of weak ties in social networks?
a. Weak ties are not important in social networks.
b. Weak ties connect different groups, facilitating the flow of new information.
c. Weak ties are more trustworthy than strong ties.
d. Weak ties only exist within closely connected groups.
- In a social network, a triad refers to:
a. A group of three nodes where all are connected.
b. A set of three nodes connected by a single edge.
c. A group of three nodes with no connections.
d. A set of three nodes, with exactly two connected.
- Neighborhood overlap in a graph is best described as:
a. The number of edges between two nodes.
b. The number of common neighbors two nodes share.
c. The degree of a node.
d. The shortest path between two nodes.
- In the context of social network analysis, a bridge is:
a. An edge that connects two components.
b. An isolated node in the graph.
c. A node that connects two communities.
d. An edge that connects two nodes with no common neighbors.
- A local bridge is an edge that:
a. Connects two nodes with high degree.
b. Has the highest betweenness centrality in the graph.
c. Connects two nodes that have few or no other connections between them.
d. Connects two nodes that belong to the same community.
- In the context of social networks, embeddedness refers to:
a. The number of connections a node has.
b. The degree to which a relationship is supported by a network of other relationships.
c. The isolation of a node in the network.
d. The shortest path between two nodes in the graph.
- A structural hole in a network refers to:
a. A complete graph with no isolated nodes.
b. A gap between two groups that are not directly connected.
c. A node with the highest centrality in the network.
d. A cluster of nodes that are all connected to each other.
- Social capital in a network context refers to:
a. The total number of edges in the graph.
b. The sum of all the connections a node has.
c. The resources available to an individual through their social connections.
d. The average degree of the nodes in the network.
- In the brute-force method for community detection, the number of possible ways to divide a graph with nn nodes into two distinct communities is:
a. —
b. —
c. —
d. —
- The Girvan-Newman algorithm for community detection works by:
a. Removing edges with the lowest betweenness centrality.
b. Removing edges with the highest degree.
c. Removing edges with the highest betweenness centrality.
d. Randomly removing edges until the network splits into communities.
Course Link: Click Here
Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers (July-Dec 2023)
Q1. Given each node in the following Figure 4 represents an individual, a solid line between the nodes represents the existing friendship and the dotted line represents the formation of a new friendship, Which of the following is the reason for such a friendship?
Triadic Closure
Membership closure
Focal closure
selection closure
Answer: Triadic Closure
Q3. Choose the correct statement.
Clustering Coefficient denotes the probability of two nodes to become friends with each other
Triadic Closure phenomenon is rare in all kinds of networks
There is no likelihood for a person to become friend in future if he is not a friend in the present
Acquaintances lead to strong ties
Answer: Clustering Coefficient denotes the probability of two nodes to become friends with each other
Q3. In Girvan Newman Algorithm, Edge G-H get removed after D-E what does this imply?
G-H has high betweenness than D-E
D-E has high betweenness than G-H
G-H has more shortest paths
Both edge are of same betweenness
Answer: D-E has high betweenness than G-H
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Q4. Let us consider Node A has strong tie with B and C, Violation of strong Triadic closure takes place when there is ——– edge between two neighbours.
One
No
One strong
One weak
Answer: No
Q5. Which edge will be removed first based on Girvan Newman method?
3-7
4-5
4-6
1-2
Answer: 3-7
Q6. The measure of betweenness centrality is based on the
longest path through node
shortest path through node
longest path between node and high degree node
shortest path between node and high degree node
Answer: shortest path through node
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 3 Assignment 3 Answers
Q7. What role/property of social networks is at display here in network K?
I. Structural hole
II. V2 monopolises
III. Brokerage
I and II only
II and III only
I and III only
I, II and III
Answer: I, II and III
Q8. Consider two nodes with P and Q set of friends each, the equation |P∩Q|/|P∪Q|describes the
Clustering coefficient
Social Capital
Neighbourhood Overlap
Centrality Measure
Answer: Neighbourhood Overlap
Q9. Given that neighbourhood overlap of an edge m is equal to 0. Then m is
a strong tie
a local bridge
edge with high betweenness
a triad
Answer: a local bridge
These are Nptel Social Networks Week 3 Assignment 3 Answers
Q10. What is the embeddedness between the nodes v0 and v2 in the given friendship network?
0
1
2
3
Answer: 3
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
More Weeks of Social Networks: Click here
More Nptel Courses: Click here
Session: JAN-APR 2023
Course Name: Social Networks
Course Link: Click Here
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Q1. Which of the following algorithm is used to detect communities in a network?
a. Girvan Newman
b. Page Rank
c. Hits
d. Both Girvan Newman and Page Rank
Answer: a. Girvan Newman
Q2. Identify the mechanism that ensures if two people in a social network have a friend in common, then there is an increased likelihood that they will become friends themselves at some point in the future.
a. Social Capital
b. Structural hole
c. Triadic closure
d. Neighborhood overlap
Answer: c. Triadic closure
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Q3. Which of the following is True for the edge AB in Graph H?
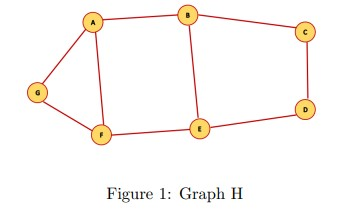
I. It is a strong tie
II. It is a local bridge
III. It is a weak tie
a. Only I
b. Both I and II
c. Both II and III
d. I, II and III
Answer: c. Both II and III
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Q4. Compute the embeddedness of the edge AB in the graph H in Figure 1.
a. 0
b. 1
c. 3
d. 4
Answer: a. 0
Q5. Find the Neighborhood overlap of of the edge connecting V0 and V2 in the graph P. in Figure 2
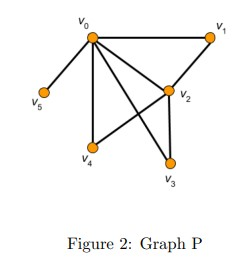
a. 3/5
b. 3/4
c. 1/4
d. 1
Answer: b. 3/4
Q6. Consider a large social network where we have two communities that are connected by only through two nodes P and Q. Apart from being a weak tie, this also exhibits a property called
a. Social Capital
b. Structural hole
c. Triadic closure
d. Neighborhood overlap
Answer: b. Structural hole
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Q7. We have a community A supporting a popular hero A and another community B that supports a popular hero B in Facebook, we see that they play an important role that makes the content on Facebook all the more popular. Identify those properties.
a. Closure
b. less diameter
c. High density
d. Brokerage
Answer: a, d
Q8. Which of the following conditions is ideal for a good community?
a. ratio of intra-community edges to inter-community edge should be high
b. ratio of intra-community edges to inter-community edge should be low
c. ratio of intra-community edges to inter-community edge should be 1
d. ratio of intra-community edges to inter-community edge should be 0
Answer: a. ratio of intra-community edges to inter-community edge should be high
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
Q9. Pick out the statement that best describes betweenness centrality.
a. All the shortest paths between the given node and the highest degree node.
b. All the longest paths between the given node and the highest degree node.
c. All the shortest paths that pass through the given node.
d. All the longest paths that pass through the given node.
Answer: c. All the shortest paths that pass through the given node.
Q10. While implementing the Girvan Newman algorithm on a certain graph G, you observe that edge E1 gets removed after edge E2. What can you comment about them?
a. E1 has higher betweenness than E2
b. E2 has higher betweenness than E1
c. E2 has higher embeddedness than E1
d. E1 has higher embeddedness than E2
Answer: b. E2 has higher betweenness than E1
These are Social Networks Week 3 Nptel Assignment Answers
More Solutions of Social Networks: Click Here
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers/
