Deep Learning | Week 9
Course Name: Deep Learning
Course Link: Click Here
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q1. Suppose Elina has trained a neural network 3 times (Experiment A, B and C) with some
unknown optimizer. Each time she has kept all other hyper-parameters same, but changed only
one hyper-parameter. From the three given loss curves, can you identify what is that hyper-
parameter?
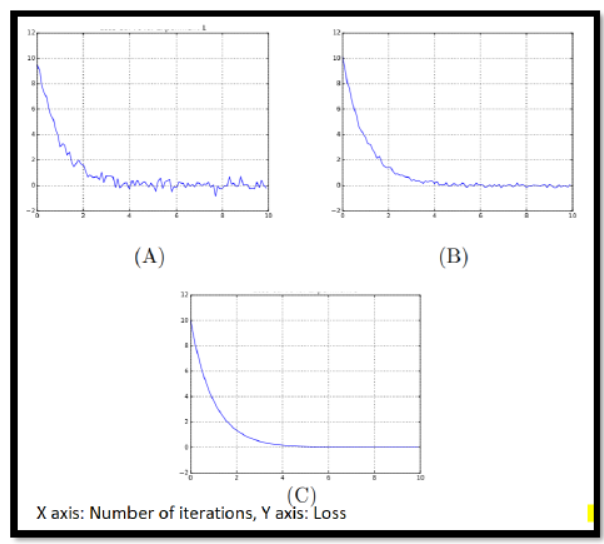
a. Batch size
b. Learning rate
c. Number of hidden layers
d. Loss function
Answer: a. Batch size
Q2. This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements.
Statement 1: Mini-batch gradient descent will always overshoot the optimum point even with a lower learning rate value.
Statement 2: Mini-batch gradient might oscillate in its path towards convergence and oscillation can reduced by momentum optimizer.
a. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is False
b. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is True
c. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is True
d. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is False
Answer: b. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is True
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q3. This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements.
Statement 1: Apart from the learning rate, Momentum optimizer has two hyper parameters whereas Adam has just one hyper parameter in its weight update equation
Statement 2: Adam optimizer and stochastic gradient descent have the same weight update rule
a. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is False
b. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is True
c. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is True
d. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is False
Answer: d. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is False
Q4. Which of the following options is true?
a. Stochastic Gradient Descent has noisier updates
b. In Stochastic Gradient Descent, a small batch of sample is selected randomly instead of the whole data set for each iteration. Too large update of weight values leading to faster convergence
c. In big data applications Stochastic Gradient Descent increases the computational burden
d. Stochastic Gradient Descent is a non-iterative process
Answer: a. Stochastic Gradient Descent has noisier updates
or
c. In big data applications Stochastic Gradient Descent increases the computational burden
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q5. Which of the following is a possible edge of momentum optimizer over of mini-batch gradient descent?
a. Mini-batch gradient descent performs better than momentum optimizer when the surface of the loss function has a much more elongated curvature along X-axis than along Y-axis
b. Mini-batch gradient descent always performs better than momentum optimizer
c. Mini-batch gradient descent will always overshoot the optimum point even with a lower learning rate value
d. Mini-batch gradient might oscillate in its path towards convergence which can reduced by momentum optimizer
Answer: d. Mini-batch gradient might oscillate in its path towards convergence which can reduced by momentum optimizer
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q6. Which of the following is true?
a. Adam is a replacement optimization algorithm for stochastic gradient descent for training deep learning models in local minima
b. Apart from the learning rate, Momentum optimizer has two hyper parameters whereas Adam has just one hyper parameter in its weight update equation
c. Adam optimizer and stochastic gradient descent have the same weight update rule
d. None of the above
Answer: a. Adam is a replacement optimization algorithm for stochastic gradient descent for training deep learning models in local minima
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q7. Which of the following is the correct property of RMSProp optimizer?
a. RMSProp divides the learning rate by an exponentially decaying average of squared gradients
b. RMSProp has a constant learning rate
c. RMSProp divides the learning rate by an exponentially increasing average of squared gradients
d. RMSProp decays the learning rate by a constant value
Answer: a. RMSProp divides the learning rate by an exponentially decaying average of squared gradients
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q8. Why it is at all required to choose different learning rates for different weights?
a. To avoid the problem of diminishing learning rate
b. To avoid overshooting the optimum point
c. To reduce vertical oscillations while navigating the optimum point
d. This would aid to reach the optimum point faster
Answer: d. This would aid to reach the optimum point faster
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q9. This question has Statement 1 and Statement 2. Of the four choices given after the statements, choose the one that best describes the two statements.
Statement 1: The stochastic gradient computes the gradient using a single sample
Statement 2: It converges much faster than the batch gradient
a. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is False
b. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is True
c. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is True
d. Statement 1 is False and Statement 2 is False
Answer: c. Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is True
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q10. What is the main purpose of auxiliary classifier in GoogleNet?
a. To increase the number of parameters
b. To avoid vanishing gradient problem
c. To increase the inference speed
d. None of the above
Answer: b. To avoid vanishing gradient problem
These are NPTEL Deep Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
More weeks of Deep Learning: Click Here
More Nptel Courses: https://progiez.com/nptel
