Introduction to Machine Learning | Week 9
Session: JAN-APR 2024
Course name: Introduction to Machine Learning
Course Link: Click Here
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q1. (One or more correct options) Consider the Markov Random Field given below. We need to delete one edge (without deleting any nodes) so that in the resulting graph, B and F are independent given A. Which of these edges could be deleted to achieve this independence? Note: In each option, we only delete one edge from the original graph.
AC
BE
CE
AE
Answer: CE
Q2. (One or more correct options) Consider the Markov Random Field from question 1. We need to delete one node (and also delete the edges incident with that node) so that in the resulting graph, B and C are independent given A. Which of these nodes could be deleted to achieve this independence? Note: In each option, we only delete one node and its incident edges from the original graph.
D
E
F
None of the above
Answer: D
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q3. (One or more correct options) Consider the Markov Random Field from question 1. Which of the nodes has / have the largest Markov blanket (i.e. the Markov blanket with the most number of nodes)?
A
B
C
D
E
F
Answer: A
Q4. (One or more correct options) Consider the Bayesian Network given below. Which of the following independence relations hold?
A and B are independent if C is given
A and B are independent if no other variables are given
C and D are not independent if A is given
A and F are independent if C is given
Answer: c), d)
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q5. In the Bayesian Network from question 4, assume that every variable is binary. What is the number of independent parameters required to represent all the probability tables for the distribution?
8
12
16
24
36
Answer: 24
Q6. (One or more correct options) Consider the Bayesian Network from question 4. which of the given options are valid factorizations to calculate the marginal P (E = e) using variable elimination (need not be the optimal order)?
a) ∑BP(B)∑AP(A)∑DP(D|A)∑CP(C|A,B)∑FP(E=e|C)P(F|C)
b) ∑AP(A)∑DP(D|A)∑BP(B)∑CP(C|A,B)∑FP(E=e|C)P(F|C)
c) ∑BP(B)∑AP(D|A)∑DP(A)∑FP(C|A,B)∑CP(E=e|C)P(F|C)
d) ∑AP(B)∑BP(D|A)∑DP(A)∑FP(C|A,B)∑CP(E=e|C)P(F|C)
e) ∑AP(A)∑BP(B)∑CP(C|A,B)∑DP(D|A)∑FP(E=e|C)P(F|C)
Answer: b), c), d), e)
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q7. (One or more correct options) Consider the MRF given below. Which of the following factorization(s) of P(a,b,c,d,e)
satisfies/satisfy the independence assumptions represented by this MRF?
a) P(a,b,c,d,e)=1Zψ1(a,b,c,d)ψ2(b,e)
b) P(a,b,c,d,e)=1Zψ1(b)ψ2(a,c,d)ψ3(a,b,e)
c) P(a,b,c,d,e)=1Zψ1(a,b)ψ2(c,d)ψ3(b,e)
d) P(a,b,c,d,e)=1Zψ1(a,b)ψ2(c,d)ψ3(b,d,e)
e) P(a,b,c,d,e)=1Zψ1(a,c)ψ2(b,d)ψ3(b,e)
f) P(a,b,c,d,e)=1Zψ1(c)ψ2(b,e)ψ3(b,a,d)
Answer: d), f)
Q8. (One or more correct options) The following figure shows an HMM for three time steps i=1,2,3
.
Suppose that it is used to perform part-of-speech tagging for a sentence. Which of the following statements is/are true?
The Xi variables represent parts-of-speech and the Yi variables represent the words in the sentence.
The Yi variables represent parts-of-speech and the Xi variables represent the words in the sentence.
The Xi variables are observed and the Yi variables need to be predicted.
The Yi variables are observed and the Xi variables need to be predicted.
Answer: The Yi variables represent parts-of-speech and the Xi variables represent the words in the sentence.
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
More Weeks of Introduction to Machine Learning: Click here
More Nptel Courses: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers
Session: JULY-DEC 2023
Course Name: Introduction to Machine Learning
Course Link: Click Here
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q1. Which of the following best describes the Markov property in a Hidden Markov Model (HMM)?
The future state depends on the current state and the entire past sequence of states.
The future state depends only on the current state and is independent of the past states, given the current state.
The future state depends on the past states and the future states, given the current state.
The future state depends only on the past states and is independent of the current state.
Answer: The future state depends only on the current state and is independent of the past states, given the current state.
Q2. Statement 1: Probability distributions are valid potential functions.
Statement 2: Probability is always strictly positive.
Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 2 is the correct reason for statement 1.
Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is true. Statement 2 is not the correct reason for statement 1.
Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
Both statements are false.
Answer: Statement 1 is true. Statement 2 is false.
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q3. In the undirected graph given below, which nodes are conditionally independent of each other given B? Select all that apply.
C, D
D, E
E, C
A, F
None of the above
Answer: A [C, D], C [E, C]
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q4. Given graph below:
Factorization is:
p(x,y,z)=p(x)p(y|x)p(y|z)
p(x,y,z)=p(y)p(x|y)p(z|y)
p(x,y,z)=p(z)p(z|y)p(x|y)
p(x,y,z)=p(y)p(y|x)p(y|z)
Answer: p(x,y,z)=p(y)p(x|y)p(z|y)
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q5. For the given graphical model, what is the optimal variable elimination order when trying to calculate P(E=e)?
A, B, C, D
D, C, B, A
A, D, B, C
D, A, C, A
Answer: A, B, C, D
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q6. Which of the following methods are used for calculating conditional probabilities? (more than one may apply)
Viterbi algorithm
MAP inference
Variable elimination
Belief propagation
Answer: C, D
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q7. In the undirected graph given below, which nodes are conditionally independent of each other given a single other node (may be different for different pairs)? Select all that apply.
3, 2
0, 4
2, 5
1, 5
Answer: A, D
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
More Weeks of INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING: Click here
More Nptel Courses: Click here
Session: JAN-APR 2023
Course Name: Introduction to Machine Learning
Course Link: Click Here
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q1. Consider the bayesian network shown below.
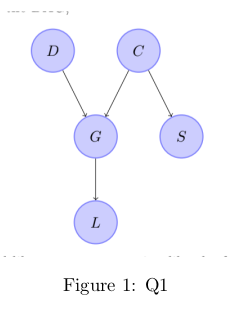
Two students – Manish and Trisha make the following claims:
• Manish claims P(D|{S,L,C})=P(D|{L,C})
• Trisha claims P(D|{S,L})=P(D|L)
where P(X|Y) denotes probability of event X given Y. Please note that Y can be a set. Which of the following is true?
a. Manish and Trisha are correct.
b. Manish is correct and Trisha is incorrect.
c. Manish is incorrect and Trisha is correct.
d. Both are incorrect.
e. Insufficient information to make any conclusion. Probability distributions of each variable should be given.
Answer: b. Manish is correct and Trisha is incorrect.
Q2. Consider the same bayesian network shown in previous question (Figure 1). Two other students in the class – Trina and Manish make the following claims:
• Trina claims P(S|{G,C})=P(S|C)
• Manish claims P(L|{D,G})=P(L|G)
Which of the following is true?
a. Both the students are correct.
b. Trina is incorrect and Manish is correct.
c. Trina is correct and Manish is incorrect.
d. Both the students are incorrect.
e. Insufficient information to make any conclusion. Probability distributions of each variable should be given.
Answer: a. Both the students are correct.
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q3. Consider the Bayesian graph shown below in Figure 2.
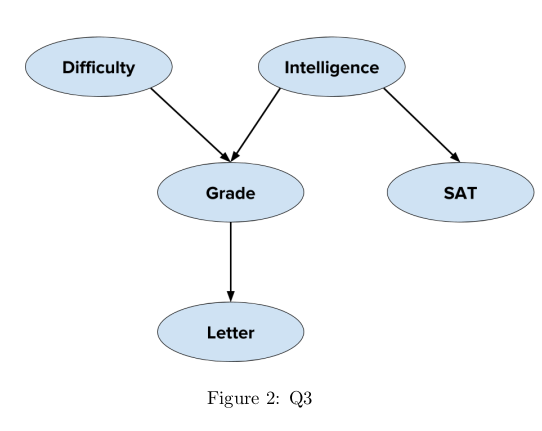
The random variables have the following notation: d – Difficulty, i – Intelligence, g – Grade, s -SAT, l – Letter. The random variables are modeled as discrete variables and the corresponding CPDs are as below.
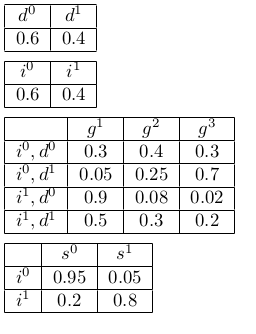
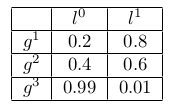
What is the probability of P(i=1,d=0,g=2,s=1,l=1)?
a. 0.004608
b. 0.006144
c. 0.001536
d. 0.003992
e. 0.009216
f. 0.007309
g. None of these
Answer: e. 0.009216
Q4. Using the data given in the previous question, compute the probability of following assignment, P(i=1,g=1,s=1,l=0) irrespective of the difficulty of the course? (up to 3 decimal places)
a. 0.160
b. 0.371
c. 0.662
d. 0.047
e. 0.037
f. 0.066
g. 0.189
Answer: d. 0.047
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q5. Consider the Bayesian network shown below in Figure 3
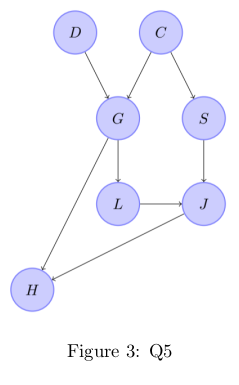
Two students – Manish and Trisha make the following claims:
• Manish claims P(H|{S,G,J})=P(H|{G,J})
• Trisha claims P(H|{S,C,J})=P(H|{C,J})
Which of the following is true?
a. Manish and Trisha are correct.
b. Both are incorrect.
c. Manish is incorrect and Trisha is correct.
d. Manish is correct and Trisha is incorrect.
e. Insufficient information to make any conclusion. Probability distributions of each variable should be given.
Answer: d. Manish is correct and Trisha is incorrect.
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q6. Consider the Markov network shown below in Figure 4
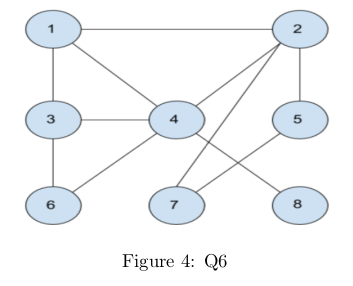
Which of the following variables are NOT in the markov blanket of variable “4” shown in the above Figure 4 ? (multiple answers may be correct)
a. 1
b. 8
c. 2
d. 5
e. 6
f. 4
g. 7
Answer: d, f, g
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q7. In the Markov network given in Figure 4, two students make the following claims:
• Manish claims variable “1” is dependent on variable “7” given variable “2”.
• Trina claims variable “2” is independent of variable “6” given variable “3”.
Which of the following is true?
a. Both the students are correct.
b. Trina is incorrect and Manish is correct.
c. Trina is correct and Manish is incorrect.
d. Both the students are incorrect.
e. Insufficient information to make any conclusion. Probability distributions of each variable should be given.
Answer: d. Both the students are incorrect.
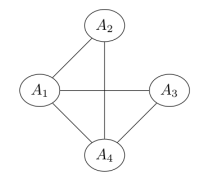
Q8. Four random variables are known to follow the given factorization
P(A1=a1,A2=a2,A3=a3,A4=a4)=1Zψ1(a1,a2)ψ2(a1,a4)ψ3(a1,a3)ψ4(a2,a4)ψ5(a3,a4)
The corresponding Markov network would be
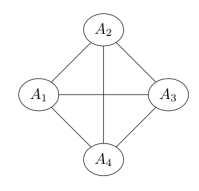
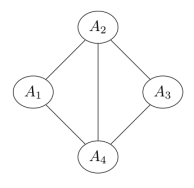
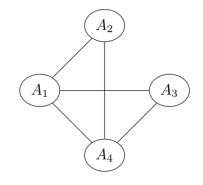
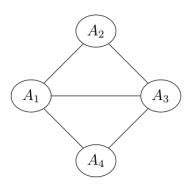
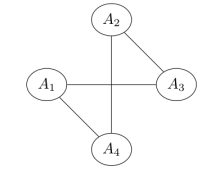
Answer: c.
Q9. Does there exist a more compact factorization involving less number of factors for the distribution given in previous question?
a. Yes
b. No
c. Insufficient information
Answer: a. Yes
Q10. Consider the following Markov Random Field.
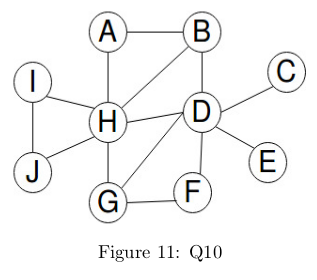
Which of the following nodes will have no effect on H given the Markov Blanket of H?
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
Answer: C, E, F
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
More Weeks of Introduction to Machine Learning: Click Here
More Nptel courses: https://progiez.com/nptel
Session: JUL-DEC 2022
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Course Name: INTRODUCTION TO MACHINE LEARNING
Link to Enroll: Click Here
Q1. In the undirected graph given below, which nodes are conditionally independent of each other given B? Select all that apply.

a. A, D
b. D, E
c. C, D
d. A, F
e. None of the above
Answer: a. A, D
Q2. In the modified undirected graph given below, which nodes are conditionally independent of each other given B? Select all that apply.

a. C, D
b. D, E
c. E, C
d. A, F
e. None of the above
Answer: c. E, C
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q3. In the undirected graph given below, how many terms will be there in its potential function factorization?

a. 7
b. 3
c. 5
d. 9
e. None of the above
Answer: b. 3
Q4. Which of these can be modeled as a HMM? Select all that apply.
a. Machine translation
b. Speech recognition
c. Trajectory of a baseball
d. Fibonacci sequence
Answer: d. Fibonacci sequence
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q5. HMMs are used for finding these. Select all that apply.
a. Probability of a given observation sequence
b. All possible hidden state sequences given an observation sequence
c. Most probable observation sequence given the hidden states
d. Most probable hidden states given the observation sequence
Answer: b. All possible hidden state sequences given an observation sequence
Q6. For the given graphical model, what is the optimal variable elimination order when trying to calculate P(E=e)?

a. A, B, C, D
b. D, C, B, A
c. A, D, B, C
d. D, A, C, A
Answer: d. D, A, C, A
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
Q7. What is the tree width for the GM in previous question?
a. 5
b. 4
c. 3
d. 2
Answer: c. 3
Q8. Belief propagation is used for
a. Calculating map estimate
b. Calculating joint probability
c. Calculating conditional marginal
d. None of the above
Answer: b. Calculating joint probability
These are Introduction to Machine Learning Week 9 Assignment 9 Answers
More NPTEL Solutions: https://progiez.com/nptel
