DataBase Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers 2026

Are you looking for Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers 2026 ? You are here at right place for Week 1 assignment answers
Table of Contents

Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers (Jan-Apr 2026)
Que.1 Which of the following statements is (are) incorrect?
a) The physical level specifies how data is actually stored on disk.
b) The logical level focuses on user-specific views of the data.
c) The view level conceals details of data representation from applications.
d) The logical level defines relationships among stored data.
Que.2 Consider the following relations and relational algebra expressions. Which of the following is correct?
a) RA₁ ⊂ RA₂
b) RA₂ ⊂ RA₁
c) RA₁ ⊆ RA₂
d) RA₁ = RA₂
Que.3 Given the relation Library(BookID, MemberID, BorrowDate, ReturnDate), which tuple cannot be inserted if one tuple already exists?
a) B101, M303, 01-Jan-2026, 10-Jan-2026
b) B101, M202, 15-Jan-2026, 20-Jan-2026
c) B202, M202, 05-Jan-2026, 12-Jan-2026
d) B202, M303, 05-Jan-2026, 12-Jan-2026
Que.4 In the relation ConferenceAttendee(AttendeeID, Email, Name, SessionID), which attribute set cannot be a super key?
a) {AttendeeID}
b) {Email, SessionID}
c) {AttendeeID, Name}
d) {Email, Name}
Que.5 Identify the correct selection operation that produces the given output from the MovieDetails table.
a) σ(Genre=’Action’ ∧ Rating=9)
b) σ(Genre=’Action’ ∨ Rating=9)
c) σ(Genre=’Drama’)
d) σ(Rating ≥ 9)
Que.6 From MovieDetails₁ and MovieDetails₂, which relational algebra operation produces only the common rows?
a) MovieDetails₁ − MovieDetails₂
b) MovieDetails₂ − MovieDetails₁
c) (MovieDetails₁ ∪ MovieDetails₂) ∩ (MovieDetails₁ ∩ MovieDetails₂)
d) (MovieDetails₁ − MovieDetails₂) ∪ (MovieDetails₂ − MovieDetails₁)
Que.7 Which of the following can serve as a candidate key for the MovieDetails relation?
a) {Rating}
b) {MovieTitle}
c) {Genre}
d) {MovieTitle, Rating}
Que.8 Which relational algebra operation extracts only MovieTitle and Rating from MovieDetails?
a) σ(Rating > 8)
b) MovieDetails × MovieDetails
c) MovieDetails ⋈ Genre=’Drama’ MovieDetails
d) π(MovieTitle, Rating)(MovieDetails)
Que.9 Identify the correct classification of the SQL statements shown.
a) S1 is DDL and S2 is DML
b) Both are DDL
c) S1 is DCL and S2 is DDL
d) Both are DML
Que.10 Identify the correct statement regarding database schemas and instances.
a) Employee(emp_id, emp_name, salary) is a database instance
b) (E101, Amit, 45000) is a relation schema
c) Department(dept_id, dept_name) defines a logical schema
d) (‘D10’, ‘Accounts’) represents a physical schema
(July-Dec 2025)
Question 1. Which level of abstraction describes how data is physically stored in the database?
a) Physical level
b) Logical level
c) View level
d) Abstraction level
Question 2. Consider the following SQL statement(s):
S1:
CREATE TABLE orders (
order_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
product_id NUMBER,
quantity NUMBER,
order_date DATE
);
S2:
INSERT INTO orders(order_id, product_id, quantity, order_date)
VALUES (1001, 45, 3, '15-JUN-2024');
Identify the correct statement.
a) S1 is a Data Definition (DDL) Query, and S2 is a Data Manipulation (DML) Query.
b) Both S1 and S2 are Data Definition (DDL) Queries.
c) S1 is a Data Control Query (DCL), and S2 is a Data Definition (DDL) Query.
d) Both S1 and S2 are Data Manipulation (DML) Queries.
Question 3. Identify the correct statement(s) about database schemas and instances.
a) Student(roll no, name, dept) represents a database instance.
b) (101, ‘John’, ‘CS’) is an example of a relation schema.
c) Course(course_id, title) defines a logical schema.
d) (‘CS101’, ‘Databases’) is an instance of a physical schema.
Question 4. Consider the following international university admissions data:
| University | Year | CourseCode | StudentName | Country | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Delhi | 2023 | CS101 | Riva Sharma | India | 2023 |
| ETH Zurich | 2022 | PH202 | Noah Miller | Switzerland | 2022 |
| University of Delhi | 2023 | ME105 | Arjun Patel | India | 2023 |
| National University of Singapore | 2024 | EE110 | Li Wei | Singapore | 2024 |
| ETH Zurich | 2023 | CS101 | Riya Sharma | Switzerland | 2023 |
Identify the valid primary key for the relation university_admissions from the given instance.
a) university and country
b) student_id and admission_year
c) university and student_id
d) student name and admission_year
Question 5. Consider the following relations:Employee(eid, ename, salary); Department (did, eid)
Consider the following relational algebra expressions:
RA1: π employees. salary, ename (Employee ⋈ Department)
RA2: π employees. salary, ename (Employee × Department)
Which of the following is correct?
a) RA1 ⊂ RA2
b) RA2 ⊂ RA1
c) RA1 = RA2
d) RA1 ≠ RA2
Question 6. Consider the relational schema StudentGrades (StudentID, CourseCode, Grade, Semester).
If the following tuple exists in an instance of StudentGrades:
(TT, CS, PN, TE)
Which of the following tuples can NOT be inserted into StudentGrades?
a)
b)
c)
d)
Question 7. Consider the following table:
| RiverName | Length | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Ganges | 2626 | India |
| Yangtze | 6300 | China |
| Nile | 6650 | Egypt |
| Mississippi | 3738 | USA |
| Volga | 3645 | Russia |
| Danube | 2636 | Germany |
| Sao Francisco | 2014 | Brazil |
Identify the correct operation(s) which produces the following output from the above relation:
| RiverName | Length | Country |
a) σ (Country = ‘Brazil’) ∨ (Length = 6500) (RiverDetails)
b) σ (Country = ‘Brazil’) ∧ (Length = 6500) (RiverDetails)
c) σ (Length > 5000) (RiverDetails)
d) σ (Country = ‘Egypt’) ∨ (Country = ‘Brazil’) (RiverDetails)
Question 8. Consider the following tables:
RiverDetails1:
| RiverName | Length | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Mississippi | 3738 | USA |
| Volga | 3645 | Russia |
| Danube | 2626 | Germany |
| Sao Francisco | 2614 | Brazil |
RiverDetails2:
| RiverName | Length | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Ganges | 2626 | India |
| Yangtze | 6300 | China |
| Amazon | 6676 | Brazil |
| Nile | 6650 | Egypt |
| Volga | 3645 | Russia |
Identify the correct operation(s) which will produce the following output:
| RiverName | Length | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Ganges | 2626 | India |
| Volga | 3645 | Russia |
a) RiverDetails2 − RiverDetails1
b) RiverDetails1 − RiverDetails2
c) (RiverDetails2 − RiverDetails1) ∪ (RiverDetails1 − RiverDetails2)
d) (RiverDetails1 ∪ RiverDetails2) ∩ (RiverDetails1 ∩ RiverDetails2)
Question 9. Which of the following can be a candidate key for the following instance?
| RiverName | Length | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Ganges | 2626 | India |
| Yangtze | 6300 | China |
| Amazon | 6675 | Brazil |
| Nile | 6650 | Egypt |
| Volga | 3645 | Russia |
| Danube | 2626 | Germany |
| Sao Francisco | 2014 | Brazil |
| Parana | 2014 | Brazil |
a) {Country}
b) {Length}
c) {RiverName}
d) {Country, Length}
Question 10. Consider the following table:
| RiverName | Length | Country |
|---|---|---|
| Yangtze | 6300 | China |
| Amazon | 6675 | Brazil |
| Mississippi | 3734 | USA |
| Volga | 3645 | Russia |
| Danube | 2626 | Germany |
| Sao Francisco | 2914 | Brazil |
| Parana | 2014 | Brazil |
Which relational algebra operation extracts only river names and their lengths?
a) σ Length > 3000 (RiverDetails)
b) π RiverName, Length (RiverDetails)
c) RiverDetails × RiverDetails
d) RiverDetails ▷ Country = ‘Brazil’ RiverDetails
(Jan-Apr 2025)
Course Link: Click Here
Que. 1: Which of the following statements is (are) incorrect?
a) Logical level abstraction defines the physical storage of data.
b) View level abstraction provides a user-friendly interface for end users.
c) Physical level abstraction focuses on the relationships among data.
d) Logical level abstraction focuses on the relationships among data.
Que. 2: Consider the following SQL statements:
sqlCopyEditINSERT INTO emp_name, dept)
VALUES (101, 'Alice', 'HR');
ALTER TABLE employees ADD count salary number(8, 2);
Identify the correct statement.
a) Both S1 and S2 are Data Manipulation (DML) Queries.
b) S1 is a Data Manipulation (DML) Query, and S2 is a Data Definition (DDL) Query.
c) Both S1 and S2 are Data Definition (DDL) Queries.
d) S1 is a Data Control Query, and S2 is a Data Definition (DDL) Query.
Que. 3: Identify the valid primary key for the relation event_registration from the given instance:
| participant_id | event_id | registration_date | status |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | E001 | 2024-01-10 | Confirmed |
| 1002 | E002 | 2024-01-11 | Pending |
| 1003 | E001 | 2024-01-10 | Confirmed |
| 1004 | E003 | 2024-01-12 | Confirmed |
| 1001 | E002 | 2024-01-14 | Pending |
a) participant_id.
b) event_id, registration_date.
c) participant_id, event_id.
d) event_id, status.
Que. 4: Identify the correct statement(s):
a) Employee(empID, empName) is an instance of a relation schema.
b) Employee(empID, empName) is an example of a physical schema.
c) (101, John) is an instance of a relation schema.
d) (101, John) is an example of a logical schema.
Que. 5: Consider a relation CityDetails(CityName, Population, CountryName) where the superkeys are as follows:
{CityName}, {CityName, Population}, {CityName, CountryName}, {CityName, Population, CountryName}.
Select the possible candidate key(s).
a) {CityName, Population, CountryName}.
b) {CityName, Population}.
c) {CityName}.
d) {CityName, CountryName}.
Que. 6: Consider the following relations:
Employee(eid, ename, salary), Department(dept_id, dept_name).
Consider the following Relational Algebras:
RA1: πEmployee.eid, ename(Employee ⨝ Department).
RA2: πEmployee.eid, ename(Employee × Department).
Which of the following is correct?
a) RA1 = RA2.
b) RA1 ⊂ RA2.
c) RA2 ⊂ RA1.
d) RA1 ≠ RA2.
Que. 7: Consider the following instance of the CourseDetails (CourseID, CourseName) relation:
| CourseID | CourseName |
|---|---|
| C101 | Mathematics |
| C102 | Physics |
If CourseID is the foreign key in the relational schema StudentEnrollments (EnrollmentID, StudentName), which of the following is a valid instance of StudentEnrollments?
a)
| EnrollmentID | CourseID | StudentName |
|---|---|---|
| E001 | C105 | Amit |
| E002 | C102 | Raj |
b)
| EnrollmentID | CourseID | StudentName |
|---|---|---|
| E001 | C102 | Amit |
| E001 | C102 | Raj |
c)
| EnrollmentID | CourseID | StudentName |
|---|---|---|
| NULL | C102 | Amit |
| E003 | C102 | Raj |
d)
| EnrollmentID | CourseID | StudentName |
|---|---|---|
| E001 | C102 | Amit |
| E002 | C102 | Raj |
Que. 8: Identify the correct operation(s) to produce the following output:
Given table CityDetails:
| CityName | Population | StateName |
|---|---|---|
| Mumbai | 20000 | Maharashtra |
| Delhi | 19000 | Delhi |
| Bengaluru | 12000 | Karnataka |
a) σ (CityDetails).
b) σ (Population > 10000) ∧ (StateName = ‘Maharashtra’) (CityDetails).
c) σ (StateName = ‘Delhi’) (CityDetails).
d) π (CityDetails).
Que. 9)
Consider the following tables:
| CityName | Population | StateName |
|---|---|---|
| Delhi | 20000 | Maharashtra |
| Ahmedabad | 8000 | Gujarat |
| Pune | 6000 | Maharashtra |
| Bengaluru | 12000 | Karnataka |
| Chennai | 10000 | Tamil Nadu |
From the above tables, identify the correct operation(s) that produce the following output:
| CityName | Population | StateName |
|---|---|---|
| Mumbai | 20000 | Maharashtra |
| Ahmedabad | 8000 | Gujarat |
Options:
A) CityDetails1 ∩ CityDetails2
B) CityDetails1 - CityDetails2
C) CityDetails2 - CityDetails1
D) CityDetails1 ∪ CityDetails2
Que. 10)
Consider the following table:
| CityName | Population | StateName |
|---|---|---|
| Mumbai | 20000 | Maharashtra |
| Delhi | 19000 | Delhi |
| Bengaluru | 12000 | Karnataka |
| Hyderabad | 10000 | Telangana |
| Ahmedabad | 8000 | Gujarat |
| Pune | 6000 | Maharashtra |
Identify the correct operation(s) that produce the following output from the above relation:
| CityName | StateName |
|---|---|
| Mumbai | Maharashtra |
| Delhi | Delhi |
| Bengaluru | Karnataka |
Options:
A) π(CityName, StateName)
B) σ(Population > 12000)
C) π(CityName, StateName) ⨝ σ(Population > 12000) (CityDetails)
D) σ(CityName, StateName) (CityDetails)
(Jul-Dec 2024)
Course Link: Click Here
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers
Q1. Consider the SQL statement(s) below:
S1:
CREATE table students( student_id number(5), student_name varchar2(20), address varchar2(20), emailid varchar2(20));
S2:
DELETE FROM students WHERE student_id = 10005;
Identify the correct statement.
a) Both S1 and S2 are Data Definition (DDL) Queries
b) Both S1 and S2 are Data Manipulation (DML) Queries
c) S1 is a Data Definition (DDL) Query and S2 is a Data Manipulation Query (DML)
d) S1 is a Data Control Query and S2 is a Data Manipulation (DML) Query
Q2. Identify the valid primary key for the relation students.
a) student_id
b) student_name
c) student_name, address
d) student_id, dept_name
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers
Q3. Identify the correct statement/s.
a) Logical schema defines the overall logical structure of the database.
b) Logical schema defines the overall physical structure of the database.
c) Physical schema defines the overall logical structure of the database.
d) View schema defines the interaction between end-user and database.
Answer: a) Logical schema defines the overall logical structure of the database.
d) View schema defines the interaction between end-user and database.
Q4. Consider a relation MountainDetails (MountainName, Altitude, StateName) where the su- perkeys are as follows: (MountainName}, {MountainName, Altitude}, {MountainName, StateName}, {MountainName, Altitude, StateName).
Select the possible candidate key(s).
a) {MountainName, Altitude, StateName}
b) {MountainName, StateName}
c) {MountainName, Altitude}
d) {MountainName}
Answer: {MountainName}
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers
Q5. Let students (student_id, student name, address, emailid) and enrolment (student_id, dept name, enrolment_date) be two relations in a schema. The primary keys are shown underlined.
Let student_id be a foreign key in enrolment relation referring to students relation. Suppose, there is no violation of the above referential integrity constraint in the corresponding relation instances of students and enrolment.
Which one of the following relational algebra expressions would necessarily produce an empty relation?
a) Istudent_id (enrolment) Istudent_id (students)
b) Istudent_id (students) Istudent_id (enrolment)
c) Istudent_id(enrolment <> students)
d) Istudent_id (enrolment students)
Answer: a)
Q6.Which of the following statements is (are) correct?
a) View level abstraction describes how a record is stored.
b) View level abstraction hides details of data types and focuses on the interaction with the end-users.
c) Logical level abstraction describes what data is stored in a database and their relationships.
d) Physical level abstraction describes what data is stored in a database and their relationships.
Answer: b) View level abstraction hides details of data types and focuses on the interaction with the end-users.
c) Logical level abstraction describes what data is stored in a database and their relationships.
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers
Q7. Consider the following instance of the Student Details (StudentID, Student name) relation:
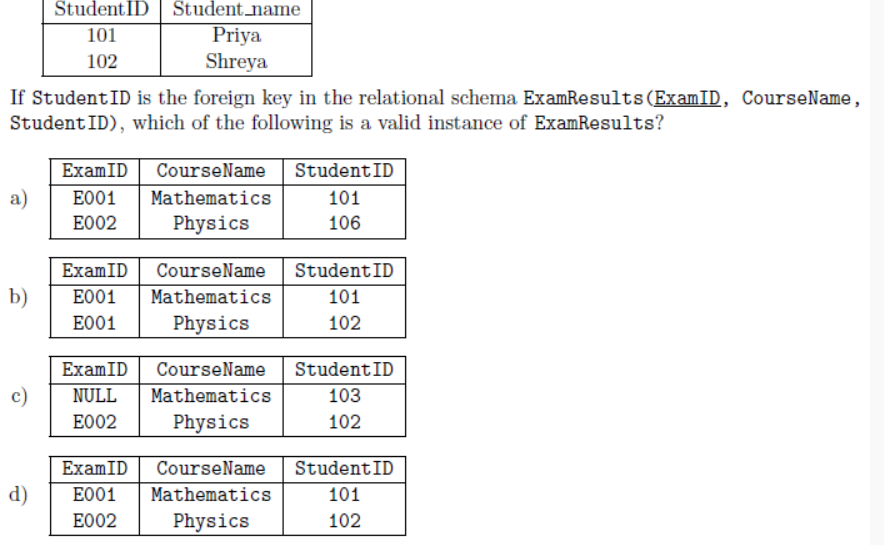
Answer : d)
Q8. Consider the following tables:
a) ChatDetails ChatDetails
b) ChatDetails2 ChatDetailsı
c) (ChatDetails ChatDetails₂) U (ChatDetails2 ChatDetails1)
d) (ChatDetails₁ U ChatDetails₂) ∩ (ChatDetails ChatDetails2)
Answer: d)
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers
Q9. Consider the following table:
a) (SenderID=1000) (ChatDetails)
b) (Total_Text>=1000) (ChatDetails)
c) II(SenderID=1000) (ChatDetails)
d) (Total_Text<=1400) (ChatDetails
Answer: b)
Q10. Consider the following table:
a) (SenderID, ReceivedID) (ChatDetails)
b) (Total Text>1000) (ChatDetails)
c) II(SenderID, ReceivedID) ((Total_Text>1000) (ChatDetails))
d) I(SenderID, ReceivedID) (ChatDetails)
Answer: c)
For answers or latest updates join our telegram channel: Click here to join
These are Data Base Management System Nptel Assignment 1 Answers
More Weeks of Data Base Management System: Click here
More Nptel Courses: https://progiez.com/nptel-assignment-answers
